-
文章精选
- 当期目录
-
过刊浏览
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volumes 54-59 (2021)
-
Volumes 48-53 (2020)
-
Volumes 42-47 (2019)
-
Volumes 36-41 (2018)
-
Volumes 30-35 (2017)
-
Volumes 24-29 (2016)
-
Volumes 18-23 (2015)
-
Volumes 12-17 (2014)
-
Volume 11 (2013)
-
Volume 10 (2012)
-
Volume 9 (2011)
-
Volume 8 (2010)
-
Volume 7 (2009)
-
Volume 6 (2008)
-
Volume 5 (2007)
-
Volume 4 (2006)
-
Volume 3 (2005)
-
Volume 2 (2004)
-
Volume 1 (2003)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
高被引
-
高下载
-
特邀文章
-
专刊合集
-
待刊文章
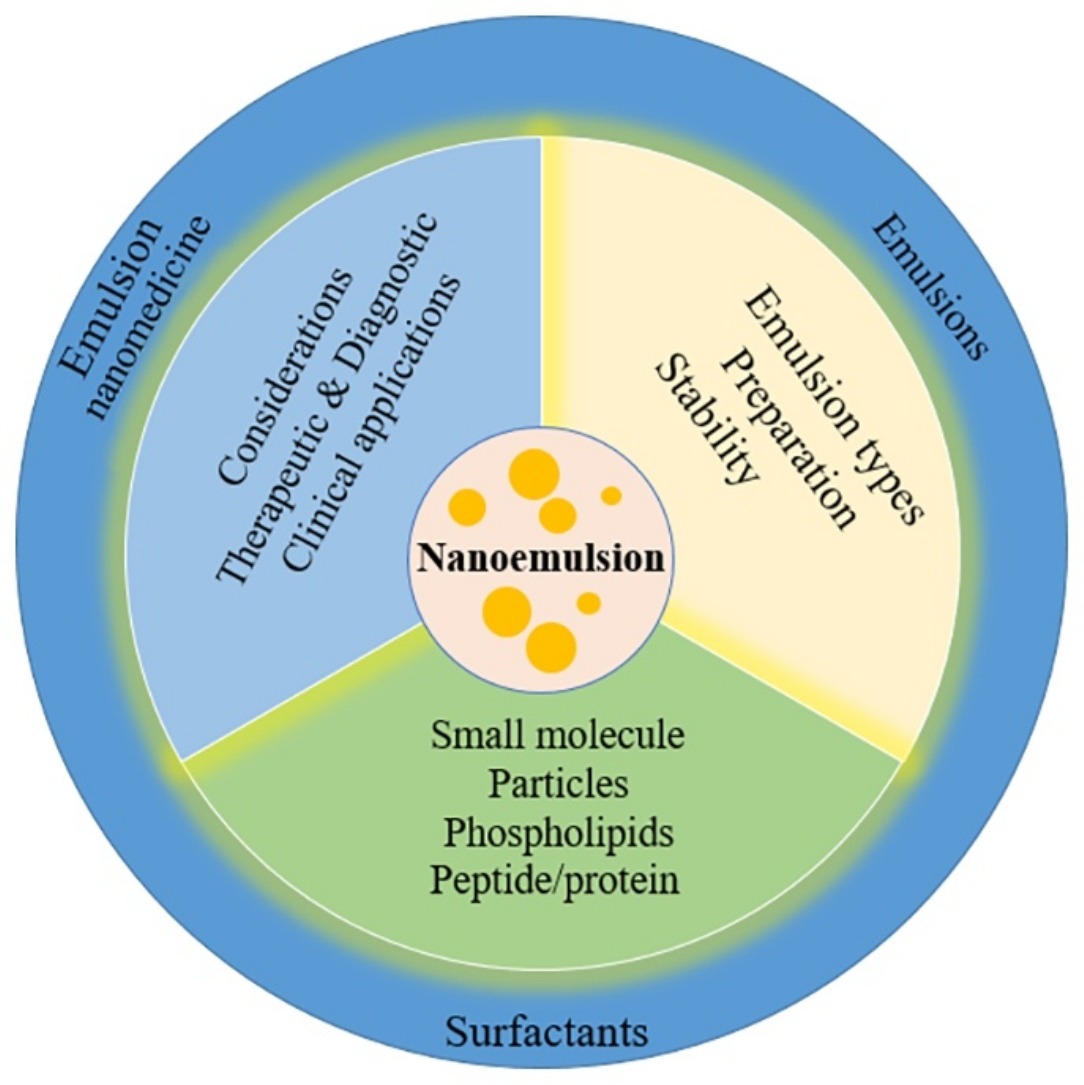
• Overview of nanoemulsions for drug delivery.
• Summary of different emulsion systems.
• Discussion about nanoemulsion preparation and stability.
• Introduction of different types of surfactants.
• Emulsion nanomedicine and their clinical applications.
Emulsions are liquid–liquid dispersions with one liquid phase dispersed in the other liquid phase as small droplets. Nanoemulsions are nano-sized emulsions with sizes ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers, and have great potential applications in pharmaceutics, foods and cosmetics due to their attractive properties, such as small sizes, high surface area per unit volume, improved dispersion of active hydrophobic components and enhanced absorption. The article provides an overview of nanoemulsions for drug delivery, starting with an introduction of emulsion types, nanoemulsion preparation and nanoemulsion stability. Surfactants play critical roles in producing and stabilizing nanoemulsions. Different types of surfactants are summarized including small molecule surfactants, particle surfactants, phospholipids, peptide and protein surfactants. Then the applications of nanoemulsions as nanomedicine in drug delivery are presented. Finally, clinical applications of nanoemulsions are discussed.