• Applications of natural enzyme face challenges of high cost and instability.
• Nanozyme features of low cost, high stability, easy manufacture and versatility.
• Nanozyme has been used as a viable enzyme alternative.
• Nanozymes are classified by enzymatic activity to explain application principle.
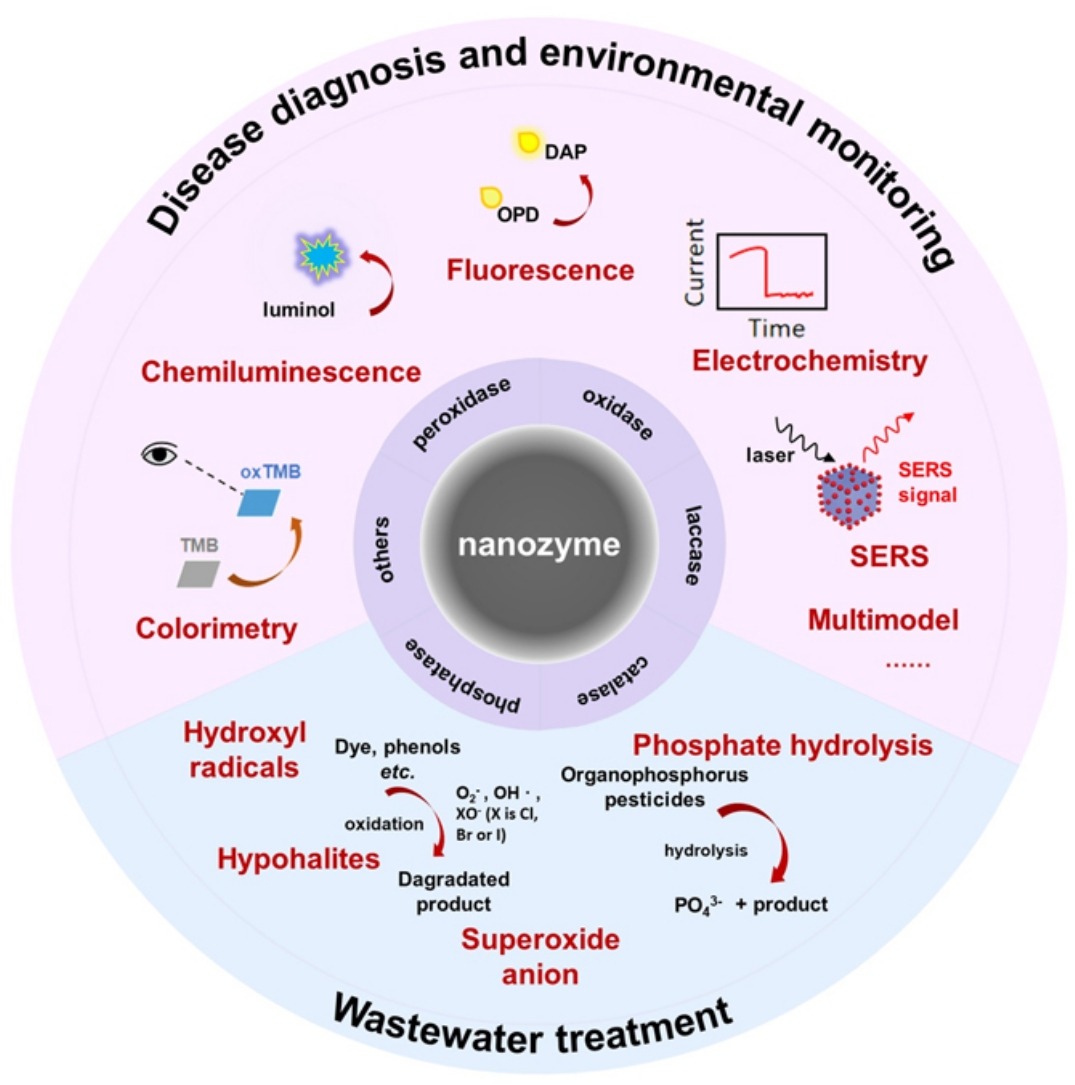
Natural enzymes, owing to their outstanding catalytic efficiency and substrate specificity, have been used in a variety of applications including clinical diagnosis, environmental monitoring and wastewater treatment. However, they face inevitable problems such as relatively high cost and lack of stability, dramatically hindering their practical applications in the industry. Recently, a class of nanomaterial that possesses intrinsic enzyme-like properties, nanozyme, has emerged exhibiting numerous advantages over its natural counterpart and has been used as a viable enzyme alternative. In the past decade there are many reviews on nanozyme. The previous discussions tend to view nanozyme as a type of nanomaterial rather than an enzyme. However, it is the enzyme-like activity of nanozymes that provides foundation for their application and nanozymes with the same enzymatic activity usually have some regularity in application. Herein, in this review, we attempt to classify nanozymes by their enzyme-like activity to explain the application principle and relevant cases of nanozymes in clinical diagnosis, environmental monitoring and wastewater treatment, expecting to promote deeper thinking of nanozymes as enzyme mimics and provide useful guidance for future research.