-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 92
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
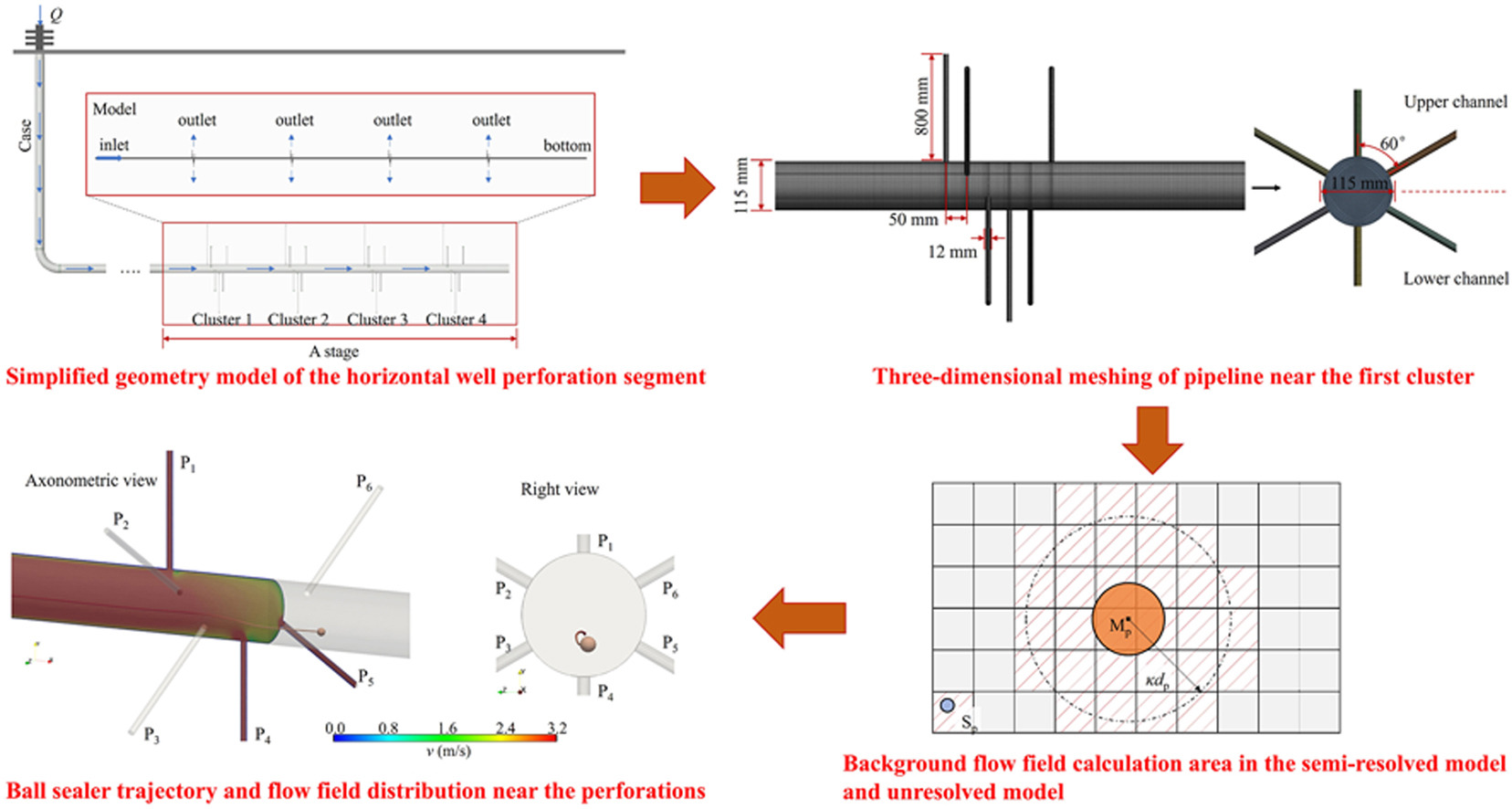
• A semi-resolved CFD-DEM model based on kernel approximation is established.
• Factors affecting the plugging probability of a single ball sealer are analyzed.
• Plugging efficiency's response to the number of ball sealers is analyzed.
• Plugging efficiency's response to the flow distribution is analyzed.
In the staged multi-cluster fracturing of shale gas horizontal wells, ball sealers are used to ensure uniform fluid distribution among clusters, a strategy that is both cost-effective and operationally beneficial. Despite these advantages, comprehending the ball sealers' dynamics within the wellbore and their plugging behavior at perforations is still challenging. This complexity results in prediction difficulties regarding their diversion efficiency. To address this, our study utilized a semi-resolved CFD-DEM model based on kernel approximation to simulate the behavior of medium-sized ball sealers in single and multiple cluster scenarios. Our findings from a single cluster scenario reveal that the plugging probability is co-determined by velocity gradients in the fluid ingestion area near the perforation, backflow region, and inertial forces of the ball sealers. As the critical flow rate is achieved, the plugging probability negatively correlated with fluid viscosity and displacement, and positively correlated with the perforation flow ratio (PFR), the difference in particle-fluid density, ball sealer's diameter, and the ball sealer's offset from the pipeline center. Temporary plugging control efficiency was used to evaluate the flow balance effect among multiple clusters. The results indicate that an increased number of ball sealers enhances the fault tolerance during the temporary plugging process. Nevertheless, excessive ball sealers might undermine the temporary plugging control efficiency, as perforations with lower fluid inflow rates are unexpectedly plugging. Higher differences in fluid injection rates between clusters led to increased efficiency in temporary plugging control. Premature deployment of ball sealers cannot effectively plug perforations with marginally higher fluid inflow rates, but instead accidently plug intermediate clusters with lower fluid inflow rates. These findings offer a theoretical basis for optimizing the design of ball sealers.