-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 92
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Reconstruction of particle distribution in Tomo-PIV via 3D CNN are explored.
• An unsupervised reconstruction technique based on U-net is proposed.
• The proposed approach outperforms traditional algebraic reconstruction techniques.
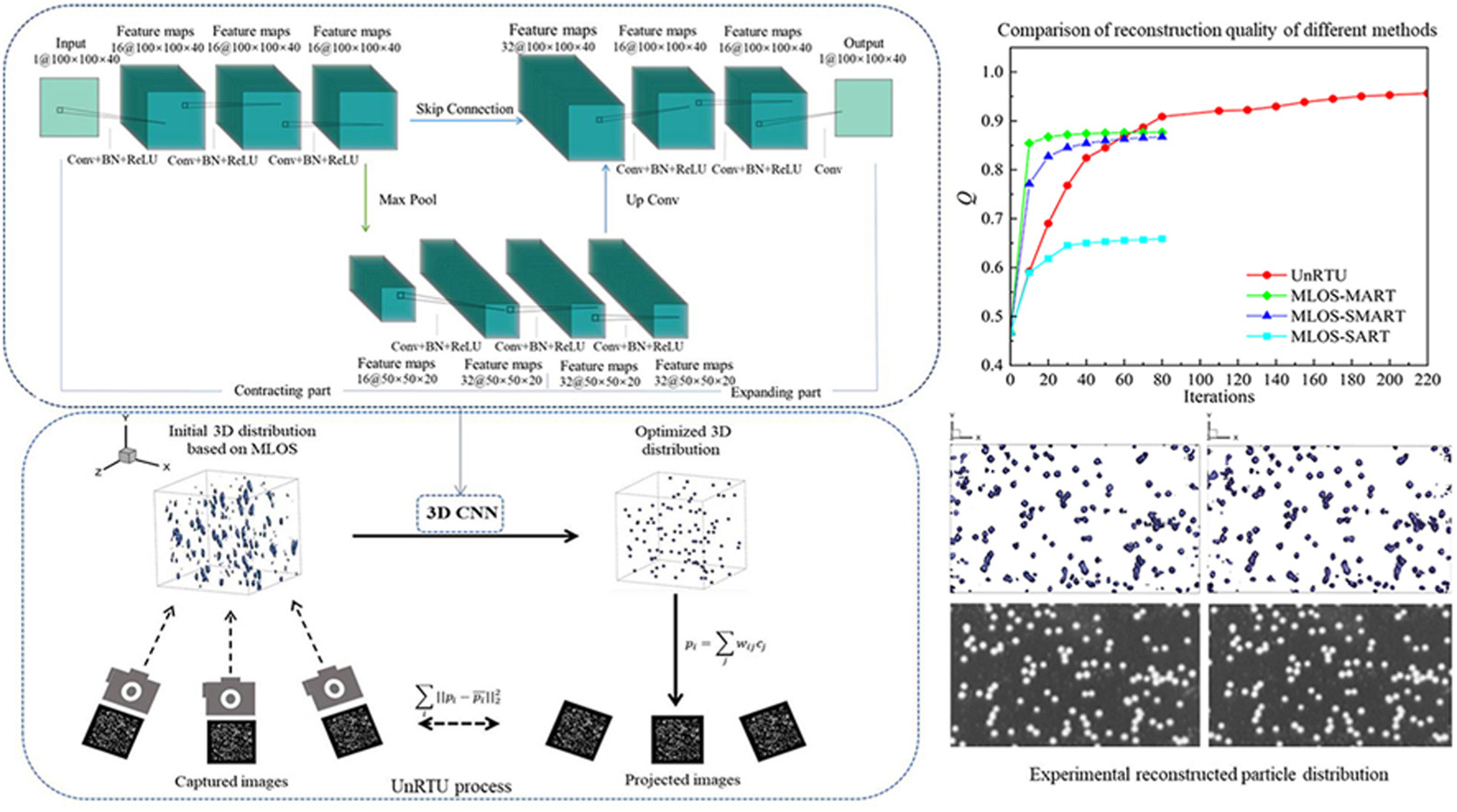
The development of deep learning has inspired some new methods to solve the 3D reconstruction problem for Tomographic Particle Image Velocimetry (Tomo-PIV). However, the supervised learning method requires a large number of data with ground truth as training information, which is very difficult to gather from experiments. Although synthetic datasets can be used as alternatives, they are still not exactly the same with the real-world experimental data. In this paper, an Unsupervised Reconstruction Technique based on U-net (UnRTU) is proposed to reconstruct volume particle distribution explicitly. Instead of using ground truth data, a projection function is used as an unsupervised loss function for network training to reconstruct particle distribution. The UnRTU was compared with some traditional algebraic reconstruction algorithms and supervised learning method using synthetic data under different particle density and noise level. The results indicate that UnRTU outperforms these traditional approaches in both reconstruction quality and noise robustness, and is comparable to the supervised learning methods AI-PR. For experimental tests, particles dispersed in cured epoxy resin are moved by an electric rail with a certain speed to obtain the ground truth data of particle velocity. Compared with other algorithms, the reconstructed particle distribution by UnRTU has the best reconstruction fidelity. And the accuracy of the 3D velocity field estimated by UnRTU is 12.9% higher than that from the traditional MLOS-MART algorithm. It demonstrates significant potential and advantages for UnRTU in 3D reconstruction of particle distribution. Finally, UnRTU was successfully applied to the high-speed planar cascade airflow field, demonstrating its applicability for measuring complex fluid flow fields at higher particle density.