- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
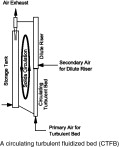
While circulating fluidized bed (CFB) reactor has many advantages over the more conventional turbulent fluidized bed (TFB) reactor, it does at least have one significant shortcoming—the rather dilute solids volume concentration in CFB reactor gives rise to less ideal reaction intensity. On the other hand, while having higher reaction intensity, TFB reactor has one fatal drawback of particle back-mixing, making it not suitable for certain reactions such as catalytic reaction where the catalyst requires frequent regeneration. This paper describes some key issues in the development of a circulating turbulent fluidized bed (CTFB) reactor that combines the advantages of both TFB and CFB, that is, to have the high reaction intensity as in TFB but and also to have a suppressed solids back-mixing as in CFB due to a continuous net upflow of solids flux through the bed. Experimental results show enough evidence to suggest that a new fluidization regime is formed, the characteristics of which appears to be distinct from those observed in a regular TFB and from those in either the bottom or the upper sections of regular CFB and/or high-density CFB (HDCFB). Fundamentally, the difference is that particle–particle interaction (collision) dominates the motion of particles in CTFB and TFB, while gas–particle interaction (drag force) is the key element that determines the two phase flow in CFB including HDCFB.