- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
Abdelghafour Zaabout a b *, Hervé Bournot a, René Occelli a, Abdeslam Draoui b
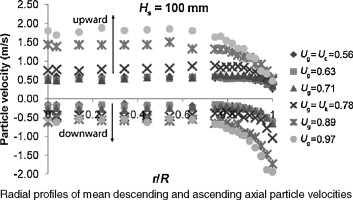
The behavior of the solid phase in the upper zone of a circulating fluidized bed riser was studied using a phase Doppler anemometer. Glass particles of mean diameter 107 μm and superficial gas velocities Ug covering the turbulent and the beginning of the fast fluidization regime were investigated. Three static bed heights were tested. Ascending and descending particles were found co-existing under all operating conditions tested, and at all measurement locations. Superficial gas velocity proved/happened to have a larger effect on descending particles at the wall and on ascending particles in the central region. Transversal particle velocities in both directions (toward the center and toward the wall) behaved relatively equivalently, with only slight difference observed at the wall. However, observation of the number of particles moving in either transversal direction showed a change in bed structure when increasing Ug. Furthermore, a balance was constantly observed between the core zone and the annulus zone where the mutual mass transfer between these two zones occurred continuously. Transition from a slow to a fast particle motion was accompanied by a transition to high levels of velocity fluctuations, and was found corresponding to the appearance of significant solid particle flow rate.