- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
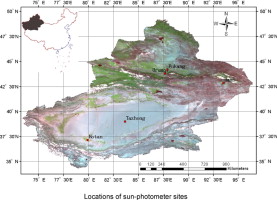
► The ground-based remote sensing of AOD from sun photometers at four sites in Xinjiang during the years 2002–2003 is used to validate aerosol products.
► The results show that MODIS C005 is superior to MODIS C004, and DB retrievals are in considerably better agreement with ground-based measurements compared with the MODIS retrievals.
The global aerosol optical depth (AOD or τ) has been retrieved using the Dark Target algorithm (the C004 and C005 products) and the Deep Blue algorithm (DB product). Few validations have thus far been performed in arid/semi-arid regions, especially in northwest China. The ground-based remote sensing of AOD from sun photometers at four sites in Xinjiang during the years 2002–2003 is used to validate aerosol products, including C004, C005 and DB of the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). The results show substantial improvement in the C005 aerosol product over the C004 product. The average correlation coefficient of regression with ground measurements increased from 0.59 to 0.69, and the average offset decreased from 0.28 to 0.13. The slopes of the linear regressions tended to be close to unity. The percentage of AODs falling within the retrieval errors of 30% (or △τ = ±0.1 ± 0.2τ) increased from 16.1% to 45.6%. The best retrievals are obtained over an oasis region, whereas the worst are obtained over urban areas. Both the MODIS C004 and C005 products overestimate AOD, which is likely related to improper assumptions of the aerosol model and of the estimation of surface reflectance. An encouraging result has been derived with regard to validation of the DB AOD. Overall, the average offset, slope and correlation coefficient of regression with sun-photometer measurements are −0.04, 0.88 and 0.85, respectively. Approximately 73% of the DB AOD retrievals fall within the expected error of 30%. Underestimation of the AOD by the DB products is observed. The aerosol model and estimations of surface reflectance in this region require further improvements.