- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
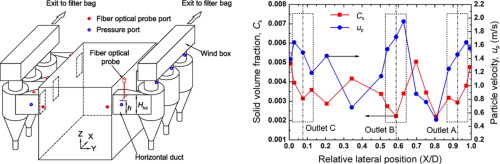
► Six cyclones were located on the left and right walls of the riser in a CFB cold test rig.
► Measurements showed that the middle cyclone on each side had higher particle velocity, but lower solid volume fraction and solid circulating rate than other two cyclones, due mainly to the non-uniform gas–solid flow at the riser outlets.
In large-scale circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers, it is common to use multiple cyclones in parallel for the capture of solids, assuming that gas–solid flow to be the same in the cyclones. This article presents a study investigating gas–solid flow through six parallel cyclones in a CFB cold test rig. The six cyclones were located asymmetrically on the left and right walls of the riser. Solid volume fraction and particle velocity profiles at the riser outlets and in the horizontal ducts were measured using a fiber optical probe. Cyclone pressure drop and solid circulating rate were measured for each individual cyclone. Measurements showed good agreement as to the non-uniform distribution of the gas–solid flow, which occurred mainly across the three cyclones on one side: the middle cyclones on both sides had higher particle velocities. Conversely, the solid volume fractions, solid fluxes and solid circulating rates of the middle cyclones were lower than those of the other four cyclones. The apparent reason for the flow non-uniformity among the cyclones is the significant flow non-uniformity at the riser outlets. Under typical operating conditions, the solid volume fractions at the riser outlets had a deviation of up to 26% whereas the solid circulating rates at the stand pipes, 7%. These results are consistent with most other studies in the literature.