- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
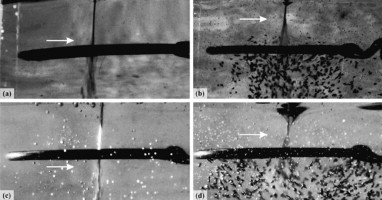
► This paper investigate jet fragmentation process when melt jet penetrates into viscose medium in the presence of a high electric field, including effects of the voltage, fluid viscosity and temperature on particle sizes, shapes and morphology.
► Applying electrohydrodynamic (EHD) force significantly reduces particle size and increases its roundness.
► Results showed that the viscosity of the dielectric environment has a significant effect on the particle size and shapes.
► The results shows that by controlling viscosity of the dielectric environment and applied voltage, size and shape of the particle could be controlled.
In this study, the breakup of a melt jet into a viscous medium is investigated in the presence of an intense electric field. Fragmentation of the melt jet occurs due to both hydrodynamic and electrohydrodynamic (EHD) forces within two kinds of silicone oil of different viscosities. The size and shape characteristics of the produced particles have been studied using SEM images, and the particle size distributions were found to exhibit considerable variations when a voltage was applied and when both the viscosity and temperature of the base fluid were changed. The morphologies of the particles were also affected by the same parameters. For instance, by applying EHD force, significant enhancements in size reduction and increased roundness of the particles occurred. The breakup process of the melt jet was found to be dominant by hydrodynamic or electrohydrodynamic instabilities, depending on the situation. Governing mechanisms (instability) in the cases of pure hydrodynamic and electrohydrodynamic fragmentations are discussed.