- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
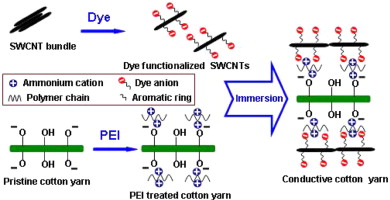
► Poly(ethylene imine) treated cotton yarn is immersed in the single walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) dispersion in Acid Red 91 solution to make SWCNTs self-assembled onto the yarn.
► The SWCNT functionalized yarn exhibits electrically conductive behaviour.
► The obtained yarn is used to make chemiresistor for detecting ammonia gas.
A simple, economical and scalable technique is demonstrated to make conductive yarn. Single walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are non-covalently functionalized with dye (Acid Red 91) and dispersed in water; while cotton yarn is treated with poly (ethylene imine). When the resulting yarn is immersed in the SWCNT dispersion, SWCNTs self-assemble onto the yarn due to electrostatic forces between the functionalized nanotubes and yarn. Scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy indicate the assembly of carbon nanotubes. The SWCNT functionalized yarn exhibits reasonable electrical conduction behaviour and are then used to make chemiresistors. The electrical resistance of the chemiresistors used as sensors increases on exposure to ammonia gas, which can be explained in terms of electron transfer between gas molecules and SWCNTs.