- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
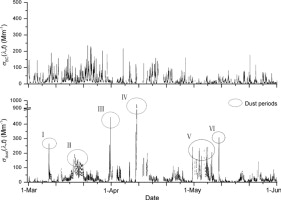
Aerosol absorption coefficient σap involves the additive contribution of both black carbon aerosol (BC) and dust aerosol. The linear statistical regression analysis approach introduced by Fialho et al. (2005) is used to estimate the absorption exponents of BC and dust aerosol absorption coefficients, and further to separate the contributions of these two types of aerosols from the total light absorption coefficient measured in the hinterland of Taklimakan Desert in the spring of 2006. Absorption coefficients are measured by means of a 7-wavelength Aethalometer from 1 March to 31 May and from 1 November to 28 December, 2006. The absorption exponent of BC absorption coefficient α is estimated as (−0.95 ± 0.002) under background weather (supposing the observed absorption coefficient is due only to BC); the estimated absorption exponent of dust aerosol absorption coefficient β during the 6 dust storm periods (strong dust storm) is (−2.55 ± 0.009). Decoupling analysis of the measured light absorption coefficients demonstrates that, on average, the light absorptions caused by dust aerosol and BC make up about 50.5% and 49.5% respectively of the total light absorption at 520 nm; during dust weather process periods (dust storm, floating dust, blowing dust), the contribution of dust aerosol to absorption extinction is 60.6% on average; in the hinterland of desert in spring, dust aerosol is also the major contributor to the total aerosol light absorption, more than that of black carbon aerosol.