- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
Zhiliang Zhang a, Yuan Le a, Jiexin Wang a, Hong Zhao a, Jianfeng Chen a b *
► IBS composite nanoparticles were prepared by using PVP/SDS as the stabilizer.
► PVP/SDS could significantly decrease the particle size to 55 nm.
► The stability of drug nanoparticles is greatly enhanced by PVP/SDS.
► The composite nanoparticles showed a significant enhancement in dissolution rate.
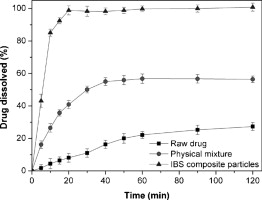
Irbesartan (IBS), an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, is a poorly water-soluble drug. To enhance the dissolution rate, IBS nanocomposite particles were produced via an anti-solvent precipitation combined with a spray drying process. Four pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, including three different polymers and one charged surfactant, were evaluated as stabilizers to control the particle size and to prevent the agglomeration of particles. The experiment results indicated that polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) combined with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) significantly decreased the particle size and enhanced the stability of drug nanoparticles. As a result, we finally obtained stable IBS nanoparticles with an average size of approximately 55 nm. In the dissolution test, the IBS nanocomposite particles showed a significantly enhanced dissolution rate and 100% of the drug dissolved within 20 min. In contrast, the physical mixture with the same recipe as the IBS nanocomposite particles and the raw IBS reached only 8% and 40% of drug dissolved in 20 min, respectively, and both of them did not dissolve completely, even after 120 min.