- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
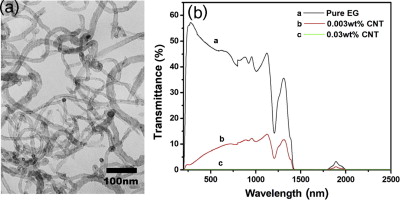
► CNTs glycol nanofluid, prepared by supersonic dispersing after oxidation treatment with HNO3, had strong absorption for sunlight.
► Enhancement of photo-thermal conversion was 18% for 0.5 wt% nanofluid at 25 °C.
► Nanofluids with 4.0 wt% CNTs exhibited lower viscosity and 25.4% higher thermal conductivity at 55 °C compared to that of pure glycol at 25 °C.
The efficiency and effectiveness of solar energy capture and storage are to a large extent functions of the heat transfer and storage capacity of the medium used. This paper investigates the potential of using carbon nanotube (CNT)-glycol nanosuspension as such a medium, prepared by freeze drying-ultrasonic dispersing after oxidation treatment with HNO3. The influences of the mass fraction of CNTs glycol nanofluids and temperatures on photo-thermal properties, thermal conductivities and rheological behavior were investigated. The results show that CNTs with oxidation treatment exhibited good dispersing performance. Strong optical absorption of the CNTs glycol nanofluids was detected in the range of 200–2500 nm. At room temperature, 18% enhancement was found in the photo-thermal conversion efficiency of the 0.5% mass fraction CNTs glycol nanofluids in comparison to the basic fluids, without significant increase in viscosity. At 55 °C, CNTs glycol nanofluids with 4.0% mass fraction exhibited much lower viscosity and 25.4% higher thermal conductivity in comparison to that of pure glycol at room temperature.