- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
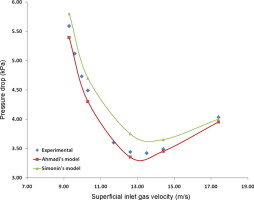
► Two-fluid model with small frictional limit boundary condition of granular flow was used.
► Turbulence interaction between gas and particle phases was investigated by Simonin's and Ahmadi's models.
► Capability of particle turbulence models was studied for dense to dilute gas–solid flows in vertical conveyor.
A two-fluid model (TFM) of multiphase flows based on the kinetic theory and small frictional limit boundary condition of granular flow was used to study the behavior of dense to dilute gas–solid flows in vertical pneumatic conveyor. An axisymmetric 2-dimensional, vertical pipe with 5.6 m length and 0.01 m internal diameter was chosen as the computation domain, same to that used for experimentation in the literature. The chosen particles are spherical, of diameter 1.91 mm and density 2500 kg/m3. Turbulence interaction between the gas and particle phases was investigated by Simonin's and Ahmadi's models and their numerical results were validated for dilute to dense conveying of particles. Flow regimes transition and pressure drop were predicted. Voidage and velocity profiles of each phase were calculated in radial direction at different lengths of the conveying pipe. It was found that the voidage has a minimum, and gas and solid velocities have maximum values along the center line of the conveying pipe and pressure drop has a minimum value in transition from dense slugging to dilute stable flow regime. Slug length and pressure fluctuation reduction were predicted with increasing gas velocity, too. It is shown that solid phase turbulence plays a significant role in numerical prediction of hydrodynamics of conveyor and the capability of particles turbulence models depends on tuning parameters of slip-wall boundary condition.