- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
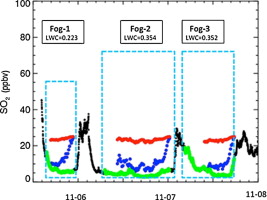
► A field experiment was conducted in a heavily SO2 polluted area located in the North China Plain.
► Large variability of SO2 was observed to be related with fog events.
► Using only effective Henry's Law constant greatly underestimates reduction of SO2 concentrations.
► To account for effect of aqueous reactions significantly improves calculated SO2 concentration.
A field experiment was conducted in an intensive fog event between November 5 and November 8, 2009, in a heavily SO2-polluted area in North China Plain (NCP), to measure SO2 and other air pollutants, liquid water content (LWC) of fog droplets, and other basic meteorological parameters. During the fog period, the concentrations of SO2 showed large variability, which was closely related to the LWC in the fog droplets. The averaged concentration of SO2 during non-fog periods was about 25 ppbv, while during the fog period, it rapidly reduced to about 4–7 ppbv. Such large reduction of SO2 suggested that a majority of SO2 (about 70%–80%) had reverted from gas to aqueous phase on account of the high solubility of SO2 in water in the fog droplets. However, the calculated gas to aqueous phase conversion was largely underestimated by merely using the Henry's Law constant of SO2, thus suggesting that aqueous reaction of SO2 in fog droplets might play some important role in enhancing the solubility of SO2. To simplify the phenomenon, an “effective solubility coefficient” is proposed in this study. This variability of SO2 measurement during the extensive fog event provides direct evidence of oxidation of SO2 in fog droplets, thus providing important implications for better understanding of the acidity in clouds, precipitation, and fogs in NCP, now a central environmental focus in China due to its rapid economic development.