- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
► Studies on environmental, health and safety (EHS) issues of nanomaterials are reviewed.
► Measurement of nanoparticle agglomerates using the Universal Nanoparticle Analyzer is discussed.
► Nanoparticle emission and exposure measurement results are presented.
► Filtration of nanoparticles and nanoparticle agglomerates is studied.
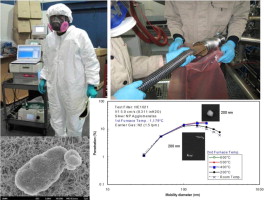
With the wide applications of nanomaterials in an array of industries, more concerns are being raised about the occupational health and safety of nanoparticles in the workplace, and implications of nanotechnology on the environment and living systems. Studies on environmental, health and safety (EHS) issues of nanomaterials play a significant role in public acceptance, and eventual sustainability, of nanotechnology. We present research results on three aspects of the EHS studies: characterization and measurement of nanoparticles, nanoparticle emission and exposure at workplaces, and control and abatement of nanoparticle release using filtration technology. Measurement of nanoparticle agglomerates using a newly developed instrument, the Universal Nanoparticle Analyzer, is discussed. Nanoparticle emission and exposure measurement results for carbon nanotubes in the manufacture of nanocomposites and for silicon nanoparticles in their production at a pilot scale facility are presented. Filtration of nanoparticles and nanoparticle agglomerates are also studied.