- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
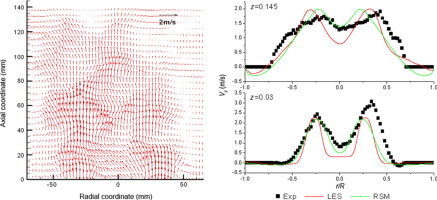
► PIV measurement with large-eddy simulation was carried out for studying swirling coal combustion.
► LES statistical results were validated by the measurement results.
► LES results show interactions among coherent structures, coal particles and flame structures.
► Effect of secondary-air ratio on NO formation was studied by the measurement results.
Particle image velocimetry (PIV), thermocouples and flue gas analyzer are used to study swirling coal combustion and NO formation under different secondary-air ratios. Eulerian–Lagrangian large-eddy simulation (LES) using the Smagorinsky–Lilly sub-grid scale stress model, presumed-PDF fast chemistry and eddy-break-up (EBU) gas combustion models, particle devolatilization and particle combustion models, are simultaneously used to simulate swirling coal combustion. Statistical LES results are validated by measurement results. Instantaneous LES results show that the coherent structures for swirling coal combustion are stronger than those for swirling gas combustion. Particles are shown to concentrate along the periphery of the coherent structures. Combustion flame is located in the high vorticity and high particle concentration zones. Measurement shows that secondary-air ratios have little effect on final NO formation at the exit of the combustor.