- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
► Defluidization with raw hematite powder was found to occur at temperature as low as 450 °C.
► Granulation reduces the tendency of defluidization, without sacrificing hematite reduction rate.
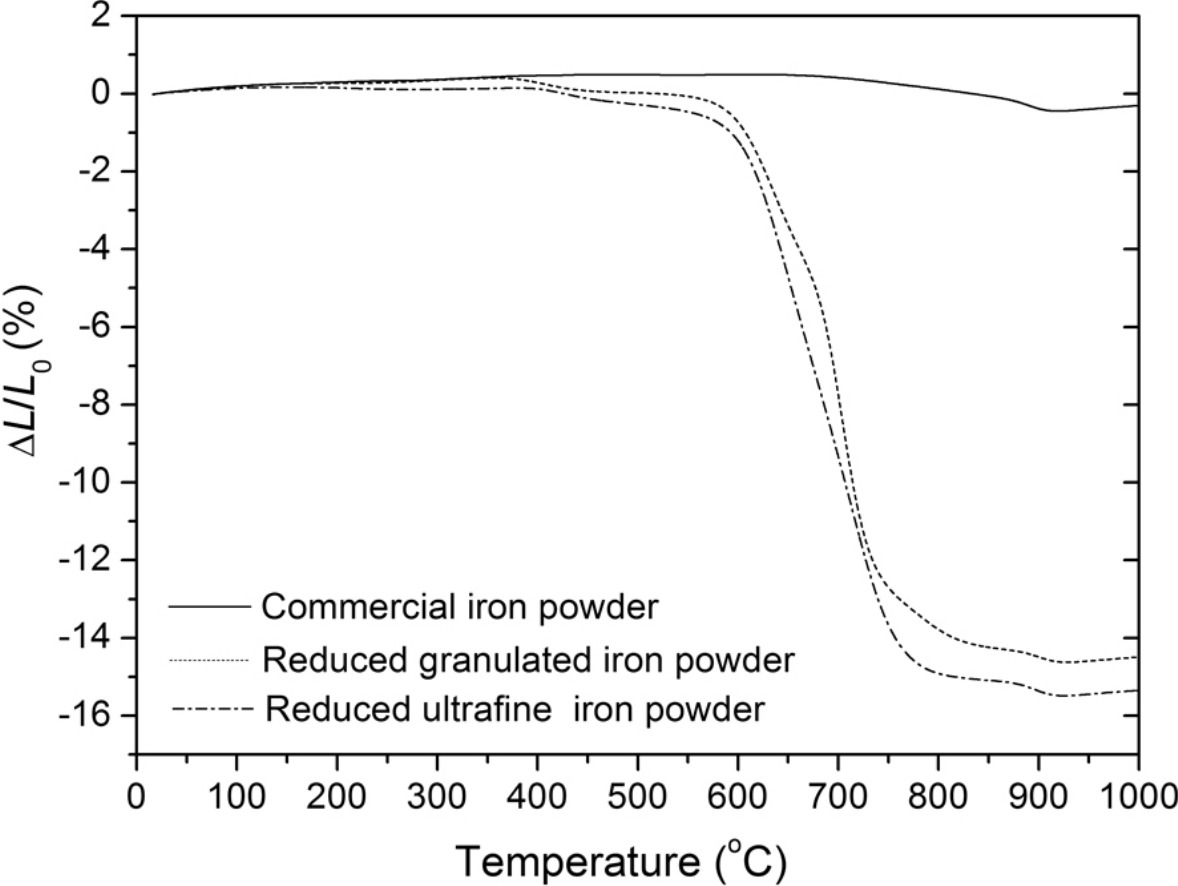
► The as-reduced iron powders exhibit excellent sintering activity.
Ultrafine hematite powder was reduced to produce ultrafine iron powder in a 50%Ar–50%H2 atmosphere at 450–550 °C in a fluidized bed reactor. The ultrafine hematite powder shows the typical agglomerating fluidization behavior with large agglomerates fluidized at the bottom of the bed and small agglomerates fluidized at the upper part of the bed. It was found that defluidization occurred even at the low temperature of 450 °C with low metallization rate. Defluidization was attributed mainly to the sintering of the newly formed iron particles. Granuation was employed to improve the fluidization quality and to tackle the defluidization problem, where granules fluidized like a Geldart's group A powder. Granulation was found to effectively reduce defluidization during reduction, without however sacrificing reduction speed. The as-reduced iron powders from both the ultrafine and the granulated hematite exhibited excellent sintering activity, that is, fast sintering at temperature of as low as ∼580 °C, which is much superior as compared to that of nano/ultrafine iron powders made by other processes.