- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
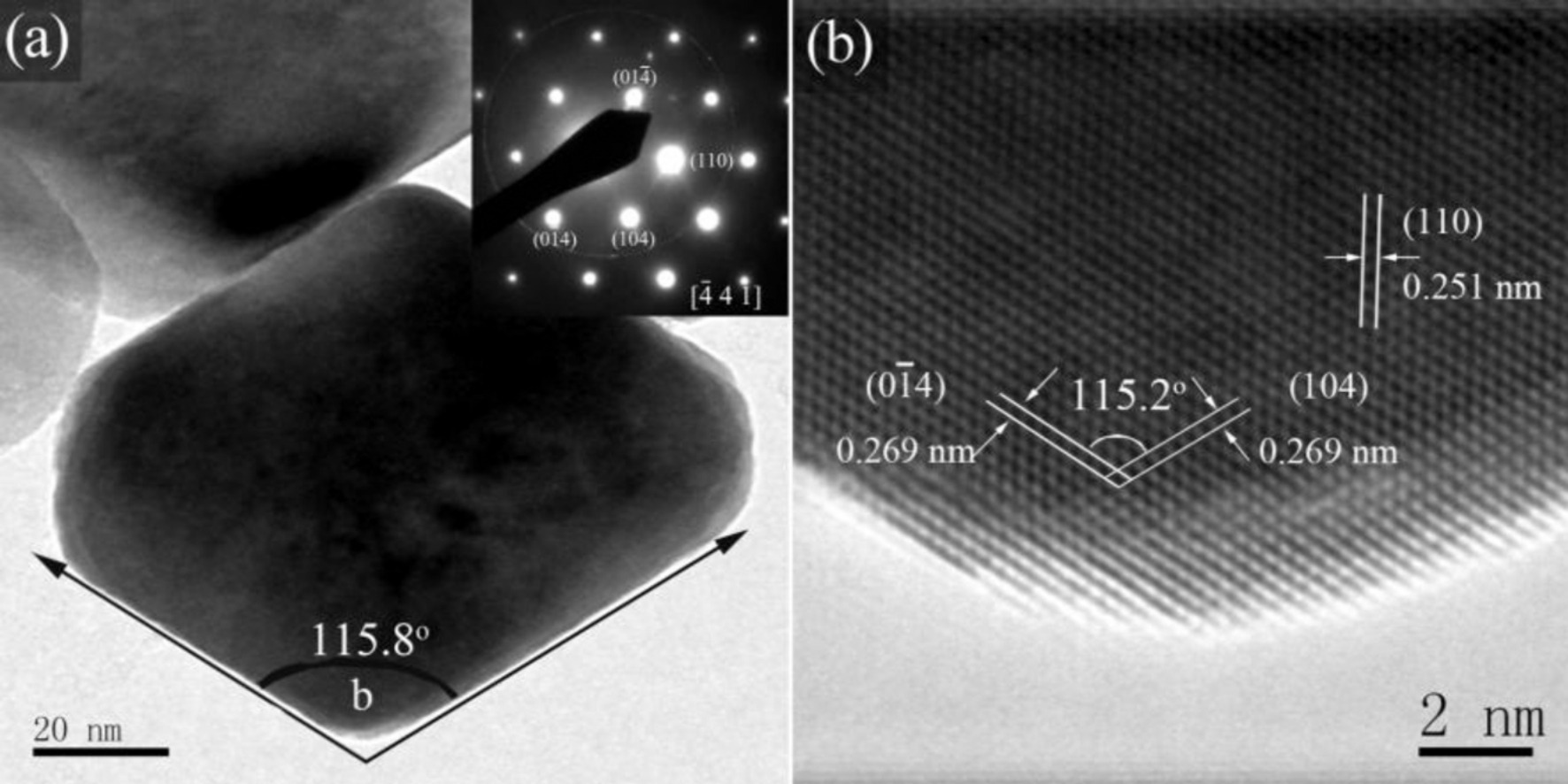
► Rhombohedral α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with a narrow size distribution (60 nm) were synthesized.
► Uniform rhombohedral α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles were enclosed by six equivalent (1 0 4) planes.
► Rhombohedral α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles showed low remanent magnetization and coercivity.
► Rhombohedral α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles exhibited good sensor capability toward H2O2.
Uniform rhombohedral α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles, ∼60 nm in size, were synthesized via a triphenylphosphine-assisted hydrothermal method. Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) and transmission electron micrograph (TEM) analyses showed that the as-synthesized rhombohedral nanoparticles were enclosed by six (1 0 4) planes. The concentration of triphenylphosphine played an important role in morphological evolution of the α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. The as-prepared rhombohedral nanoparticles possessed remanent magnetization Mr of 2.6 × 10−3 emu/g and coercivity HC of 2.05 Oe, both lower than those of other α-Fe2O3 particles with similar size, indicating their potential applications as superparamagnetic precursor materials. Furthermore, these rhombohedral α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles exhibited good sensor capability toward H2O2 with a linear response in the concentration range of 2–20 mM.