- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
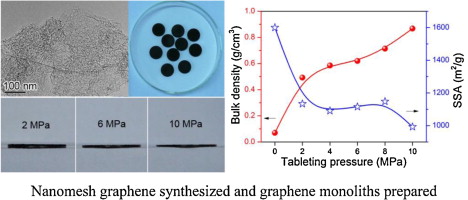
• Nanomesh graphene (NMG) was synthesized by template chemical vapor deposition.
• Binder-free graphene monoliths were prepared from loosely stacking NMG by tablet pressing.
• Graphene monoliths have obvious elasticity and a porous structure.
• Methane capacity of the graphene monolith was up to 236 (v/v) at 9 MPa.
Nanomesh graphene (NMG) obtained by template chemical vapor deposition was used to synthesize the binder-free graphene monoliths by simple tablet pressing. The stacking manner of the NMG sheets was crucial to the cohesion interaction between the graphene sheets, only the NMG materials with a loosely stacking manner could be pressed into binder-free monoliths. At the tableting pressure of 2–8 MPa, both the bulk densities and the specific surface areas of the monoliths keep nearly constant as the tableting pressure increases, indicating that the NMG monoliths have obvious elasticity and a porous structure due to the large corrugations and the mesh structures of the graphene sheets. As a result, an extraordinary methane storage capacity of 236 (v/v) at 9 MPa was obtained in the graphene monolith prepared by tableting at 4 MPa.