- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
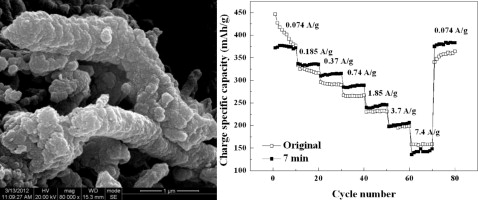
• CCVD produced P-CNFs were demonstrated as a high-rate Li storage material for LIBs.
• Reversible capacities of P-CNFs were 198.4 and 158.2 mAh/g at current density of 3.7 and 7.4 A/g.
• Carbon-coated P-CNFs were prepared by thermal vapor deposition of benzene.
• Carbon-coated P-CNFs exhibit an increased coulombic efficiency and improved cycling stability.
Carbon nanofibers with a polygonal cross section (P-CNFs) synthesized using a catalytic chemical vapor deposition (CCVD) technology have been investigated for potential applications in lithium batteries as anode materials. P-CNFs exhibit excellent high-rate capabilities. At a current density as high as 3.7 and 7.4 A/g, P-CNFs can still deliver a reversible capacity of 198.4 and 158.2 mAh/g, respectively. To improve their first coulombic efficiency, carbon-coated P-CNFs were prepared through thermal vapor deposition (TVD) of benzene at 900 °C. The electrochemical results demonstrate that appropriate amount of carbon coating can improve the first coulombic efficiency, the cycling stability and the rate performance of P-CNFs. After carbon coating, P-CNFs gain a weight increase approximately by 103 wt%, with its first coulombic efficiency increasing from 63.1 to 78.4%, and deliver a reversible capacity of 197.4 mAh/g at a current density of 3.7 A/g. After dozens of cycles, there is no significant capacity degradation at both low and high current densities.