- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Effective diffusivity, activation energy and mass transfer coefficients were studied.
• Regression analysis and ANN analysis were used to study parameter effects.
• ANN modeling was found to be suitable for assessing the correlations obtained.
• Drying kinetics of mushroom and other vegetables were compared.
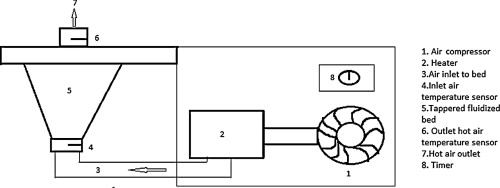
Drying characteristics in terms of diffusivity were studied for mushrooms and different vegetables in a fluidized bed dryer. Drying characteristics with falling rate regime were computed for all the samples. Effective diffusivity of each sample was calculated. Mass transfer coefficients were determined. Mass transfer kinetics for drying of different samples was also found out. Correlations for the diffusivity of samples were developed by relating the experimentally observed data with the different system parameters on the basis of regression analysis. The developed correlations for effective moisture diffusivity of the samples are validated by artificial neural network (ANN) modeling. Finally calculated values of diffusivity obtained through both the methods are compared with the experimentally measured values which show a very good approximation thereby indicating the wide applicability of the developed correlations for industrial uses.