- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
► Bulk movement of flexible filamentous particles in rotary drum was investigated with a chain model.
► Increasing flight height or drum rotational velocity could accelerate particle mixing process.
► Increase of drum loading led to a requirement of longer critical mixing time.
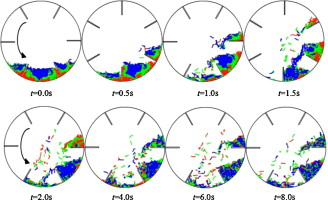
Flexible filamentous particles are a special kind of particles and play a significant role in many industrial processes. The mixing dynamics of flexible filamentous particles in the transverse section of a rotary drum were analyzed numerically in two dimensions. First, a chain model of slender bodies was introduced for particle dynamic studies, and each individual particle as well as each segment of the particle was tracked during the process. Then, the bulk movement of particles in the transverse section of a rotary drum was explored numerically and mixing dynamics of the particles were further investigated with visual representation. To quantify the quality of mixing, the mixing rates were investigated to determine the mixing extent of particles in the rotary drum. Furthermore, the effects of rotational velocity, flight height and filling degree on mixing dynamics were examined in detail. Moreover, the numerical results were compared with experimental data, and reasonable agreements were obtained. The numerical analyses provide valuable insights into the mixing dynamics of flexible filamentous particles.