- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
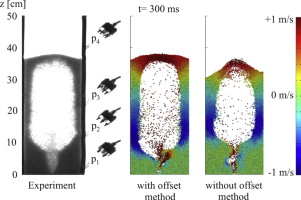
► Offset method improves calculation accuracy of fluid–particle interaction to an order of magnitude.
► Electrostatic force leads to a significant damping of the particle-wall collisions.
► Electrostatic effect causes early stabilisation state of a quasi-2D fluidized bed.
► Precise DEM simulation requires exact properties of the heterogeneous material pairing.
Dense gas–solid flow with solid volume fraction greater than 10% and at moderate Reynolds number is important in many industrial facilities such as fluidized beds. In this work, the Euler–Lagrange approach in combination with a deterministic collision model is applied to a laboratory-scale fluidized bed. The fluid–particle interaction is studied using a new procedure called the offset method, which results in several numbers of spatial displacements of the fluid grid. The proposed method is highly precise in determining porosity and momentum transfer, thus improving simulation accuracy. A validation study was carried out to assess the results using this in-house CFD/DEM code against 5-s operation of a Plexiglas spouted-fluidized bed, showing good qualitative correlation of solid distribution in the bed and acceptable quantitative agreement of pressure drops at different positions in the bed. In view of high computing cost, special emphasis is placed on effective program design, such as application of advanced detection algorithm for particle–particle/wall collisions, the multi-grid method and parallel calculation. In this context, the influence of increasing the processor number, up to 36, on calculation efficiency was investigated.