- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
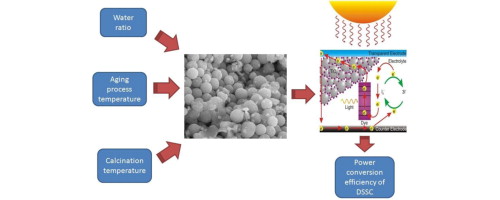
► Correlation of parameter condition and TiO2 particle's photovoltaic performance.
► Maximum DSSC performance at optimal condition of TiO2 nanoparticles preparation.
► Calcination temperature was the most significant individual and interactive parameter affecting DSSC performance.
This paper presents response surface methodology (RSM) as an efficient approach for modeling and optimizing TiO2 nanoparticles preparation via co-precipitation for dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) performance. Titanium (IV) bis-(acetylacetonate) di-isopropoxide (DIPBAT), isopropanol and water were used as precursor, solvent and co-solvent, respectively. Molar ratio of water, aging temperature and calcination temperature as preparation factors with main and interaction effects on particle characteristics and performances were investigated. Particle characteristics in terms of primary and secondary sizes, crystal orientation and morphology were determined by X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Band gap energy and power conversion efficiency of DSSCs were used for performance studies. According to analysis of variance (ANOVA) in response surface methodology (RSM), all three independent parameters were statistically significant and the final model was accurate. The model predicted maximum power conversion efficiency (0.14%) under the optimal condition of molar ratio of DIPBAT-to-isopropanol-to-water of 1:10:500, aging temperature of 36 °C and calcination temperature of 400 °C. A second set of data was adopted to validate the model at optimal conditions and was found to be 0.14 ± 0.015%, which was very close to the predicted value. This study proves the reliability of the model in identifying the optimal condition for maximum performance.