- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
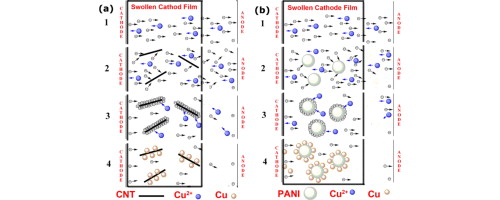
► Copper nanoparticle-anchored CNTs and PANI blocks were synthesized.
► A new kind of polymeric composites made of metal nanoparticle-anchored blocks in PVA was prepared.
► The mechanism involving this electrochemical process was speculated.
Conductive carbon nanotubes (CNTs) or alternatively polyaniline (PANI) nano-blocks was introduced into aqueous solutions of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and copper (II) salt, to assist the reduction of copper (II) ions and the anchoring of the resulting copper nanoparticles onto the conductive blocks. The mixture solutions of nano-blocks, copper (II) salts and PVA were spin-coated onto the cathode surface, forming swollen cathode films (SCFs). The copper (II) ions in the film assembled onto the surfaces of the conductive blocks and were then reduced under an appropriate voltage. It is important that the copper nanoparticles grew only on the surfaces of the conductive blocks. PVA which acted as the matrix of the composites played a role in stabilizing the resulting copper nanoparticles. Morphologies of these polymeric composite films were studied by various characterization methods. Moreover, the mechanism of migration of copper (II) ions, the formation of these polymeric composites, and the overall procedure were investigated in detail.