- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
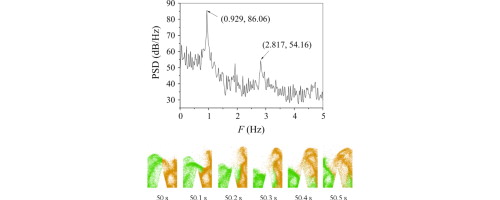
• Solid exchange in a dual-leg fluidized bed was studied with CFD-DEM model.
• The simulated particle flow patterns are similar to the experimental data.
• Two dominant frequencies exist in PSD results.
• Higher fluidization velocity results in more intensive particles exchange between the two half beds.
• Cluster exchange frequency decreases with an increase of the bed inventory.
The CFD-DEM model was developed to simulate solid exchange behavior between two half beds in a bench-scale two-dimensional dual-leg fluidized bed (DL-FB). Power spectrum density (PSD) analysis was applied to obtain the dominant frequency (F) of the simulated differential particle number (ΔPLR) between the two half beds. Effects of fluidization velocity (u) and bed material inventory (H) on the solid exchange behavior were studied using the CFD-DEM model. Not only snapshots of the simulated particle flow patterns using the OpenGL code but also the dominant frequency of ΔPLR was similar to the experimental results. The simulation results show that higher fluidization velocity assists the exchange of more particles between the two half beds, but the dispersion of clusters on the bed surface into single particles decreases the cluster exchange frequency. A greater bed material inventory results in more intense cluster exchange. The cluster exchange frequency decreases with an increase of the bed material inventory.