- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
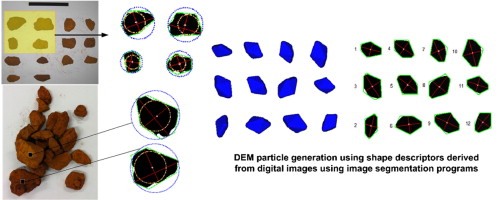
Particle shape characterisation and its application to discrete element modelling
• Two image segmentation programmes were developed to obtain particle shape descriptors.
• Separated and lumped particle images were analysed and reconstructed.
• Two-dimensional shape descriptor parameters were extracted from particles images.
• Irregularly shaped DEM particles were generated utilising the particle shape descriptors.
Increasing importance has been placed on particle shape implementation within discrete element modelling (DEM) in order to more accurately reflect the non-spherical behaviour of the bulk material being handled. As computational resources grow, complex particle shapes are increasingly being modelled as the associated simulation times become more realistic to provide timely solutions. The objective of this research is to assess particle shape descriptors through a digital image segmentation technique, and to further implement particle shape parameters into generation of corresponding irregular shaped DEM particles. Separated and lumped particle images were analysed and reconstructed through the development of two distinct methodologies. Subsequently, various particle shape descriptors were obtained using combinations of image segmentation algorithms, including mathematical morphology processing, thresholding, edge detection, region growing, region splitting and region merging. DEM particles were subsequently created using particle shape results obtained above. Shape parameters of DEM particles were then examined and validated against the real particle shape parameters.