- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
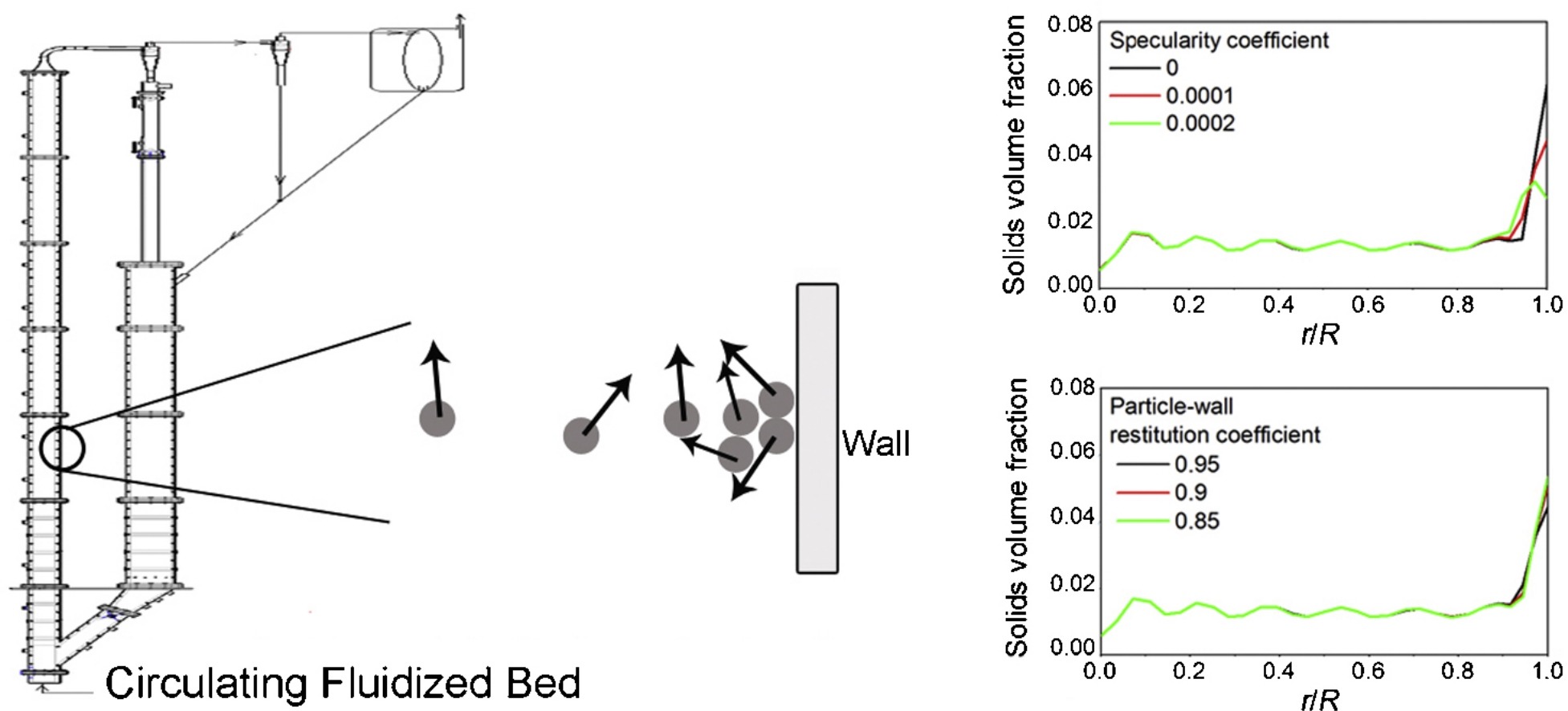
• A 2D circulating fluidized bed riser system is modeled.
• The specularity coefficient has a strong effect on the solid particle distribution near the wall.
• The particle–wall restitution coefficient has less effect on solid particle distribution near the wall than that of specularity coefficient.
• The specularity and particle–wall restitution coefficients affect the lateral velocity of the solid particles near the wall.
A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling of the gas–solids two-phase flow in a circulating fluidized bed (CFB) riser is carried out. The Eularian–Eularian method with the kinetic theory of granular flow is used to solve the gas–solids two-phase flow in the CFB riser. The wall boundary condition of the riser is defined based on the Johnson and Jackson wall boundary theory (Johnson & Jackson, 1987) with specularity coefficient and particle–wall restitution coefficient. The numerical results show that these two coefficients in the wall boundary condition play a major role in the predicted solids lateral velocity, which affects the solid particle distribution in the CFB riser. And the effect of each of the two coefficients on the solids distribution also depends on the other one. The generality of the CFD model is further validated under different operating conditions of the CFB riser.
CFD; Circulating fluidized bed; Gas–solids two-phase flow; Wall boundary condition; Specularity coefficient; Particle–wall restitution coefficient
