- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• An image method was developed for in-line measurements of dilute two-phase flow.
• Different brightness of the background needs different threshold calculation methods.
• The method is capable of simultaneously measuring particle size, velocity and concentration.
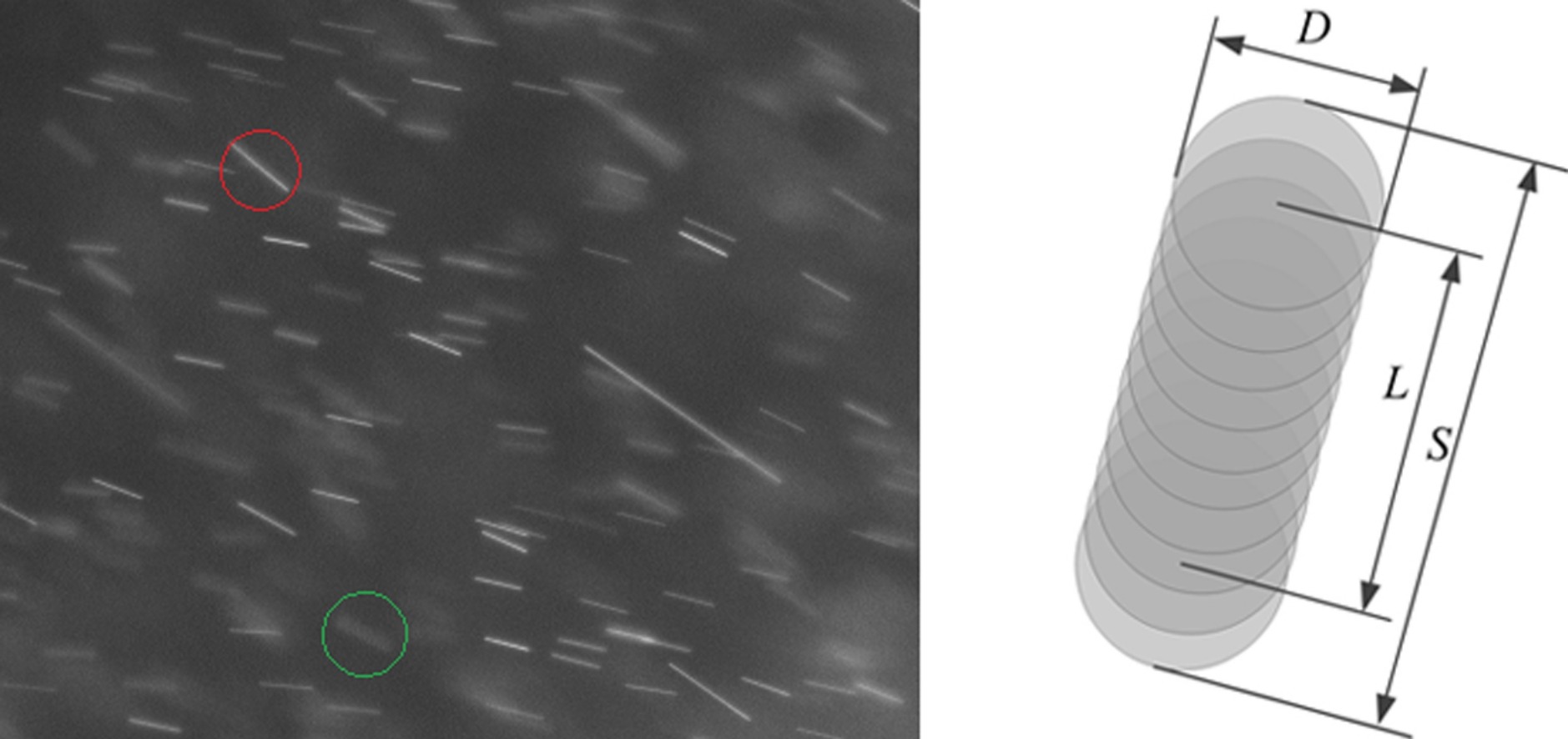
A novel method is developed for in-line measurements of particle size, velocity and concentration in a dilute, particulate two-phase flow based on trajectory image processing. The measurement system consists of a common industrial CCD camera, an inexpensive LED light and a telecentric lens. In this work, the image pre-processing steps include stitching, illumination correction, binarization, denoising, and the elimination of unreal and defocused particles. A top-hat transformation is found to be very effective for the binarization of images with non-uniform background illumination. Particle trajectories measured within a certain exposure time are used to directly obtain particle size and velocity. The particle concentration is calculated by using the statistics of recognized particles within the field of view. We validate our method by analyzing experiments in a gas-droplet cyclone separator. This in-line image processing method can significantly reduce the measurement cost and avoid the data inversion process involved in the light scattering method.
In-line measurements; Particle trajectory; Image processing; Multi-parameters
