- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• The integrating sphere used has high precision and stable radiance output.
• Comparison of calibration results with original Cimel values shows the method's credibility.
• Field measurements further validate the feasibility and precision of the calibration method.
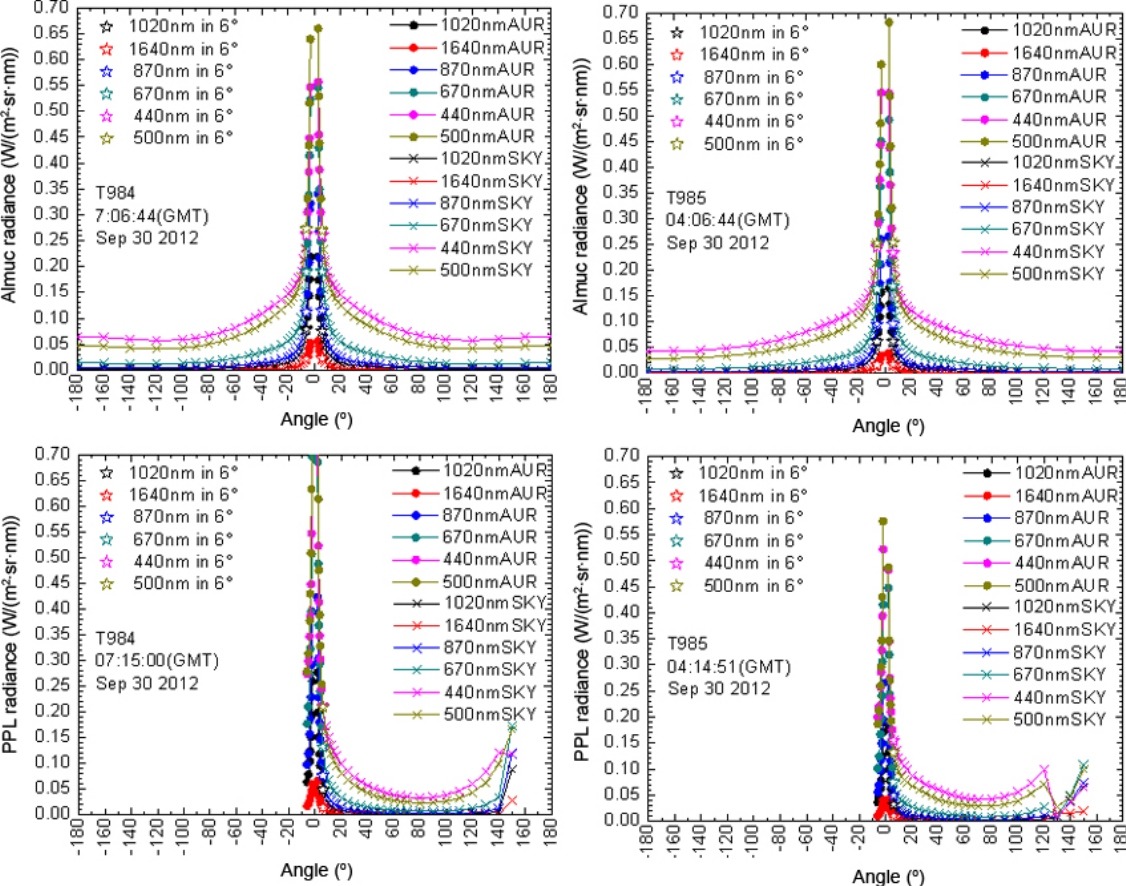
Based on the integrating sphere traced from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST, USA), a sphere calibration method and protocol for the China aerosol remote sensing network (CARSNET) Cimel sun photometer was established. Four CE318 sun photometers were verified using the proposed calibration method and operational protocol. The calibration results showed that the instrument coefficients differed by less than 3% for visible (∼5% for infrared) wavelengths from the original ones stated by Cimel Electronique. In situ validation experiment data showed that radiances at ±6° measured by sun collimator (aureole) were consistent with those measured by sky collimator (sky), under both almucantar (ALMUC) and principal plane (PPLAN) scenarios. Differences at all wavelengths were less than 1%, indicating that the method and protocol are suitable for CARSNET field sun photometer calibration, and would benefit improvement of data quality and accuracy of network observations.
CE318 sunphotometer; Integrating sphere; Calibration; CARSNET
