- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Effects of speed, load, and PPD concentration on exhaust particulate matters were studied.
• PPD could change ignition delay and decrease engine output to below that of pure diesel.
• PPD combustion had a significant impact on particle emissions and size distributions.
• Adding PPD increased the amount of nucleation mode particles emitted.
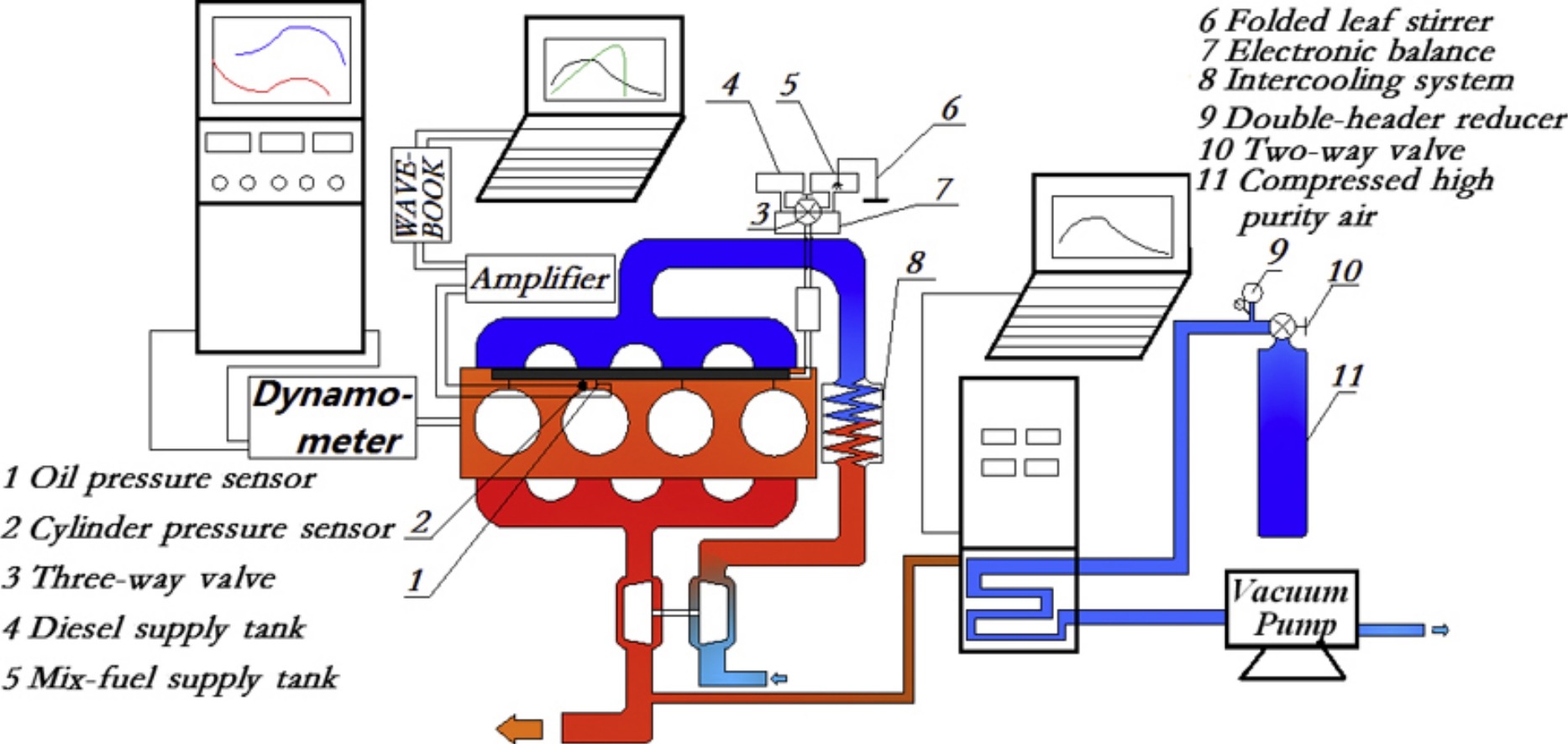
Many studies have been performed on diesel engine particulate matter emissions, but the influence of lubricants on emissions has only been considered a few times, and the effects of lubricant additives have yet to be investigated. We studied the influence of a pour point depressant additive (PPD) on particle emissions and particle size distributions from a four-cylinder turbocharged, inter-cooled engine with CF-4 15W-40 lubricant, using diesel or diesel containing the PPD. Changing the working conditions changed the number of particles emitted and the location of the peak particle size(s) emitted. The number of particles first increased and then decreased as the engine speed increased. Particle emissions were optimal at low engine speeds and high load, increasing with increasing engine speed.
Diesel; PPD; Particulate matter; Particle emission; Distribution of particles
