- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Mechanical properties for the ZSM5 zeolite particles were characterized.
• Particle bulk compression was used to show the influence of single particle mechanical properties.
• Single particle compression and nanoindentation were used for testing individual particles.
• Adams model was shown to be suitable for describing the bulk compression.
• The predicted Adams apparent strength was in good agreement with the single particle strength.
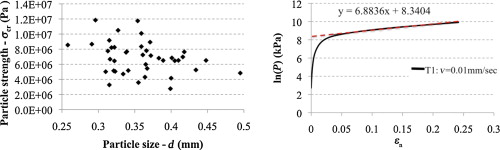
In this work typical mechanical properties for a catalyst support material, ZSM5 (a spray-dried granular zeolite), have been measured in order to relate the bulk behaviour of the powder material to the single particle mechanical properties. Particle shape and size distribution of the powders, determined by laser diffraction and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), confirmed the spherical shape of the spray-dried particles. The excellent flowability of the material was assessed by typical methods such as the Hausner ratio and the Carr index. This was confirmed by bulk measurements of the particle–particle internal friction parameter and flow function using a Schulze shear cell, which also illustrated the low compressibility of the material. Single particle compression was used to characterize single particle mechanical properties such as reduced elastic modulus and strength from Hertz contact mechanics theory. Comparison with surface properties obtained from nanoindentation suggests heterogeneity, the surface being harder than the core. In order to evaluate the relationship between single particle mechanical properties and bulk compression behaviour, uniaxial confined compression was carried out. It was determined that the Adams model was suitable for describing the bulk compression and furthermore that the Adams model parameter, apparent strength of single particles, was in good agreement with the single particle strength determined from single particle compression test.
Zeolite particle; Flowability; Powder flow function; Effective angle of internal friction; Schulze shear cell; Nanoindentation; Single particle compression; Bulk compression
