- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
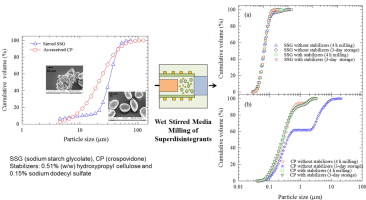
• Colloidal suspensions of superdisintegrants were prepared via wet media mill.
• The superdisintegrants used were crospovidone (CP) and sodium starch glycolate (SSG).
• Stabilizers used were hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS).
• Extensive breakage of the superdisintegrant particles occurred during milling.
• SSG suspensions were stable w/o HPC–SDS, whereas CP suspensions required HPC–SDS.
Superdisintegrants are cross-linked polymers that can be used as dispersants for fast release of drug nanoparticles from nanocomposite microparticles during in vitro and in vivo dissolution. Currently available superdisintegrant particles have average sizes of approximately 5–130 μm, which are too big for drug nanocomposite applications. Hence, production of stable superdisintegrant suspensions with less than 5 μm particles is desirable. Here, we explore the preparation of colloidal suspensions of anionic and nonionic superdisintegrants using a wet stirred media mill and assess their physical stability. Sodium starch glycolate (SSG) and crospovidone (CP) were selected as representative anionic and nonionic superdisintegrants, and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) were used as a steric stabilizer and a wetting agent/stabilizer, respectively. Particle sizing, scanning electron microscopy, and zeta potential measurements were used to characterize the suspensions. Colloidal superdisintegrant suspensions were prepared reproducibly. The extensive particle breakage was attributed to the swelling-induced softening in water. SSG suspensions were stable even in the absence of stabilizers, whereas CP suspensions required HPC–SDS for minimizing particle aggregation. These findings were explained by the higher absolute (negative) zeta potential of the suspensions of the anionic superdisintegrant (SSG) as compared with those of the nonionic superdisintegrant (CP).