- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
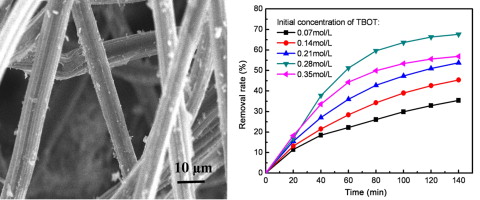
• TiO2 nanoparticles were deposited on activated carbon fibers by hydrothermal method.
• TiO2 loading could be adjusted by altering the initial concentration of TBOT.
• TiO2/ACF showed photocatalytic activity toward RhB under visible light irradiation.
• Composite fiber with 75.1% of TiO2 presented best degradation rates (67.6%).
TiO2-loaded activated carbon fibers (ACF) were prepared by a hydrothermal method. The samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometry and UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS). SEM images showed that the TiO2 nanoparticles were deposited on the surface of ACF, and the particle size and loading amount of TiO2 were varied by changing the initial concentration of tetrabutyl titanate (TBOT). The results of an ash experiment showed that the loading amounts of TiO2 were 18.4%, 43.3%, 52.5%, 75.1%, and 91.1% for initial concentrations of TBOT of 0.07, 014, 0.21, 0.28, and 0.35 mol/L, respectively. Physical interactions played an important role in the formation of TiO2/ACF composite fibers that absorb UV and visible light. Compared with those of ACF, improved adsorption and photocatalytic activity toward Rhodamine B (RhB) were observed for TiO2/ACF composite fiber. The Rhodamine B could be removed efficiently by TiO2/ACF composite fibers, and the TiO2 loading amount had a significant effect on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2/ACF composite fibers.