- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
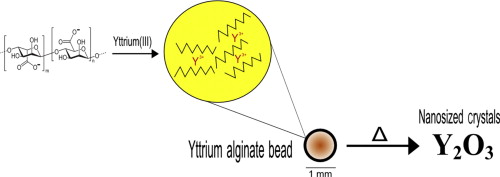
• Yttrium oxide nanopowders were synthesized by thermal decomposition of yttrium alginate.
• Effects of annealing temperature and duration on nanoparticle size were investigated.
• At the same annealing condition, the proposed method yields smaller powders than combustion method.
Yttrium oxide nanopowder was prepared by a novel technique using an alginate biopolymer as a precursor. The technique is based on thermal decomposition of an yttrium alginate gel, which is produced in the form of beads by ionic gelation between the yttrium solution and sodium alginate. The effect of post-annealing temperature on the particle size of the nanocrystals was investigated at various temperatures. The products were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and atomic force microscopy. The size of the nanocrystalline Y2O3 particles varied from 22.7 to 38.7 nm, depending on the annealing temperature and time. The grain size distribution (GSD) was also determined. The GSD became more non-symmetrical as the annealing temperature increased, and the width of the distributions for the powders produced using the alginate method was less affected by heat treatment. This alginate method was compared with the conventional glycine combustion method, on the basis of particle size. The particles obtained using the proposed technique were smaller than those obtained using the combustion method. Alginate-assisted thermal decomposition is therefore an easy and cost-effective method for preparing nanosized Y2O3 crystals.