- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
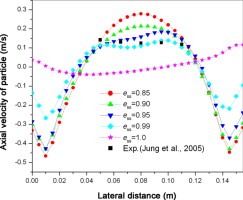
• Effect of elasticity of particle collision on fluidized bed hydrodynamics was investigated.
• Predictions with restitution coefficient of 0.95–0.99 had good agreement with experimental data.
• Assumption of perfectly elastic collision was shown to be unrealistic.
Collision between particles plays an important role in determining the hydrodynamic characteristics of gas–solid flow in a fluidized bed. In the present work, earlier work (Loha, Chattopadhyay, & Chatterjee, 2013) was extended to study the effect of the elasticity of particle collision on the hydrodynamic behavior of a bubbling fluidized bed filled with 530-μm particles. The Eulerian–Eulerian two-fluid model was used to simulate the hydrodynamics of the bubbling fluidized bed, where the solid-phase properties were calculated by applying the kinetic theory of granular flow. To investigate the effect of the elasticity of particle collision, different values of the coefficient of restitution were applied in the simulation and their effects were studied in detail. Simulations were performed for two different solid-phase wall boundary conditions. No bubble formation was observed for perfectly elastic collision. The bubble formation started as soon as the coefficient of restitution was set below 1.0, and the space occupied by bubbles in the bed increased with a decrease in the coefficient of restitution. Simulation results were also compared with experimental data available in the literature, and good agreement was found for coefficients of restitution of 0.95 and 0.99.