- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
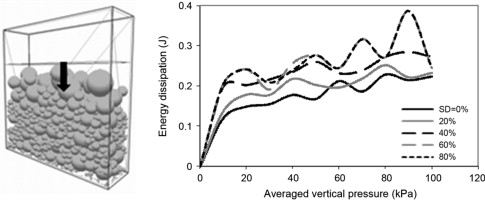
• The micromechanical properties of polydisperse granular media were investigated.
• Uniaxial compression test was modeled using discrete element method.
• Coordination number decreased with increasing the polydispersity of sphere assembly.
• Energy loss increased with increasing the standard deviation of particle mean diameter.
A series of numerical tests was conducted to study the micromechanical properties and energy dissipation in polydisperse assemblies of spherical particles subjected to uniaxial compression. In general, distributed particle size assemblies with standard deviations ranging from 0% to 80% of the particle mean diameter were examined. The microscale analyses included the trace of the fabric tensor, magnitude and orientation of the contact forces, trace of stress, number of contacts and degree of mobilization of friction in contacts between particles. In polydisperse samples, the average coordination numbers were lower than in monodisperse assemblies, and the mobilization of friction was higher than in monodisperse assemblies due to the non-uniform spatial rearrangement of spheres in the samples and the smaller displacements of the particles. The effect of particle size heterogeneity on both the energy density and energy dissipation in systems was also investigated.