- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
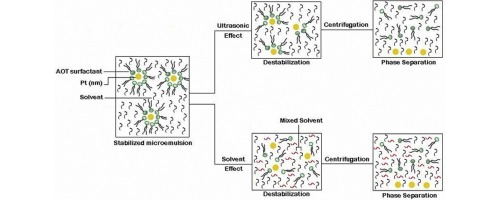
• Both ultrasonic irradiation and destabilizer solvent influenced destabilization of colloidal suspension.
• A critical irradiation time was introduced for phase separation.
• Among the four destabilizing solvents tested, tetrahydrofuran was preferable.
In this work, ultrasonic irradiation and destabilizer solvent were used for destabilizing colloidal platinum dispersions. The stabilized platinum nanoparticles were prepared in w/o microemulsion systems composed of sodium bis-(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate (AOT) and four different solvents, namely, cyclohexane, n-hexane, n-heptane, and n-nonane. The recovery process of Pt nanoparticles from the colloidal systems was performed by exposing the colloidal samples to ultrasonic irradiation and applying various destabilizing solvents. Analysis of UV–visible spectra confirms that the quantity of Pt nanoparticles removed from the suspension depends on the length of time of the ultrasonic irradiation and the nature of the microemulsion oil phase. A critical time for the ultrasonic irradiation has been introduced for the phase separation of colloidal systems. To perform the solvent study, four destabilizer solvents, namely, dioxane, ethyl acetate, diethyl ether, and tetrahydrofuran, were used for breaking the colloidal suspension of platinum nanoparticles. Based on the ‘good solvent’ and ‘poor solvent’ idea, it is verified that the effect of the destabilizer solvents on the aggregation process follows the following order: tetrahydrofuran > ethyl acetate > dioxane > diethyl ether.