- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
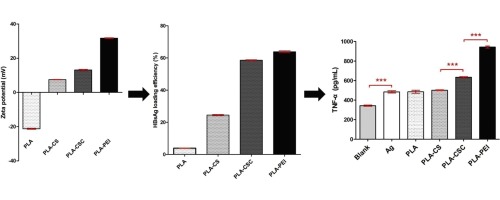
• PLA microparticles coated with various polymers were prepared, having different surface charges.
• The MPs were used as adjuvants to examine effect of surface charge on its adjuvanticity in vitro.
• HBsAg was loaded on the MPs as antigen and RAW 264.7 was used as macrophage.
• Surface charges helped to increase antigen loading, and internalization of antigen into macrophages.
• Surface charge also promoted expression of MHC II, CD80 and improved secretion level of TNF-α.
The use of microparticles (MPs) as adjuvants has attracted increasing interest in vaccine delivery systems. Many physiochemical characteristics of MPs including hydrodynamic size, surface properties, and morphology can regulate the immune response. Surface charge is an important characteristic of MPs, but how it affects their adjuvanticity remains unknown. In this study, we prepared uniform-sized polylactide MPs coated with various polymers of different positive charge, and investigated how the surface charge affected antigen loading and macrophage phagocytosis and activation in vitro. A higher surface charge greatly enhanced antigen loading and antigen internalization into macrophages, promoted the expression of MHC II and CD80, and increased the secretion level of TNF-α. Taken together, these results indicated that surface charge was an important parameter for improving the adjuvanticity of MPs.