- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
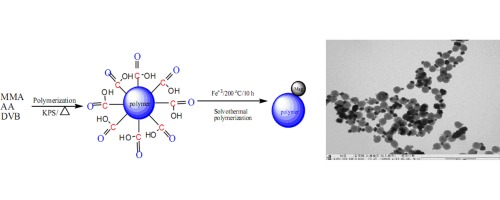
• P(MMA-AA-DVB)/Fe3O4 magnetic Janus nanoparticles were synthesized using a solvothermal process.
• Fe3O4 grew preferentially on one side of the polymeric precursor nanoparticle surface.
• Particle size was controlled to be 200 nm by adjusting amount of cross-linker in polymerization.
• Janus nanoparticles were superparamagnetic with a saturation magnetization of less than 25 emu/g.
Inorganic/organic poly(methylmethacrylate-acrylic acid-divinylbenzene) iron oxide Janus magnetic nanoparticles (P(MMA-AA-DVB)/Fe3O4) with strong magnetic domains and unique surface functionalities were prepared using a solvothermal process. The P(MMA-AA-DVB) nanoparticles were prepared via soap-free emulsion polymerization and used as a precursor for preparing Janus nanoparticles. The morphology and magnetic properties of the magnetic Janus nanoparticles formed were characterized using a laser particle size analyzer, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, and thermogravimetric analysis. The synthesized P(MMA-AA-DVB)/Fe3O4 magnetic Janus nanoparticles were characterized by a Janus structure and possessed a stable asymmetric morphology after being dually functionalized. The particle size, magnetic content, and magnetic domain of the P(MMA-AA-DVB)/Fe3O4 magnetic Janus nanoparticles were 200 nm, 40%, and 25 emu/g, respectively. The formation mechanism of the Janus nanoparticles was also investigated, and the results revealed that the reduction of Fe3+ ions and growth of Fe3O4 took place on the surface of the P(MMA-AA-DVB) polymeric precursor particles. The size of the Janus particles could be controlled by narrowing the size distribution of the P(MMA-AA-DVB) precursor nanoparticles.