- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
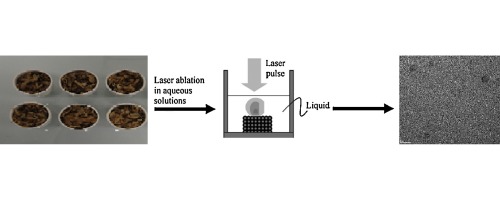
• A one-step method was developed to produce silica NPs from sugarbeet bagasse using laser ablation.
• NPs obtained by laser ablation were smaller (38–190 nm) than those prepared by NaOH treatment.
• Silica NPs thus produced have less adverse effect on C. vulgaris growth than chemically produced NPs.
Scientific research involving nanotechnology has grown exponentially and has led to the development of engineered nanoparticles (NPs). Silica NPs have been used in numerous scientific and technological applications over the past decade, necessitating the development of efficient methods for their synthesis. Recent studies have explored the potential of laser ablation as a convenient way to prepare metal and oxide NPs. Due to its high silica content, low cost, and widespread availability, sugarbeet bagasse is highly suitable as a raw material for producing silica NPs via laser ablation. In this study, two different NP production methods were investigated: laser ablation and NaOH treatment. We developed a novel, one-step method to produce silica NPs from sugarbeet bagasse using laser ablation, and we characterized the silica NPs using environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM), energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS), dynamic light scattering (DLS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR–FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy. EDS analysis and XPS confirmed the presence of silica NPs. The NPs produced by laser ablation were smaller (38–190 nm) than those produced by NaOH treatment (531–825 nm). Finally, we demonstrated positive effects of silica NPs produced from laser ablation on the growth of microalgae, and thus, our novel method may be beneficial as an environmentally friendly procedure to produce NPs.