- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
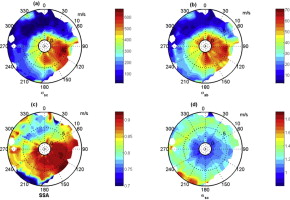
• The mean concentration of PM2.5 in Beijing in summer 2012 was 103.2 μg/m3, PM2.5/PM10 was 61.5%.
• SO42-, NO3- and NH4+ were the main ions in PM2.5 and PM10, the average NO3-/SO42- was 0.8.
• The mean values of σsc and σab were 312.9 and 28.7 Mm−1, respectively. The mean SSA was 0.85.
• The IMPROVE reconstructed σsc agreed well with the measured σsc.
• Ammonium sulfate was the largest contributor to dry σsc, followed by OM and ammonium nitrate.
The optical properties of aerosols and their chemical composition, including water-soluble ions, organic carbon (OC), and elemental carbon (EC) in PM2.5 and PM10, were measured from 26 May to 30 June of 2012 at an urban site in Beijing. The daily average concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 were 103.2 and 159.6 μg/m3, respectively. On average, the OC and EC contributed 20.1% and 4.3%, respectively, to PM2.5 and 16.3% and 3.9%, respectively, to PM10. Secondary ions (SO42-, NO3- and NH4+) dominated the water-soluble ions and accounted for 57.9% and 62.6% of PM2.5 and PM10, respectively. The wind dependence of PM2.5, OC, SO42-, and NO3- implied that the pollution sources mainly came from south and southeast of Beijing during the summer. The monthly mean values of the scattering coefficient (σsc) and absorption coefficient (σab) at 525 nm were 312.9 and 28.7 Mm−1, respectively, and the mean single-scattering albedo (ω) was 0.85. The wind dependence of σsc revealed that this value was mainly influenced by regional transport during the summer, and the relationship between σab and wind indicated that a high σab resulted from the joint effects of local emissions and regional transport. The reconstructed σsc that was derived from the revised IMPROVE equation agreed well with the observations. The contribution of different chemical species to σsc was investigated under different pollution levels, and it was found that secondary inorganic aerosols accounted for a large part of σsc during pollution episodes (35.7%), while organic matter was the main contributor to σsc under clean conditions (33.6%).