- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
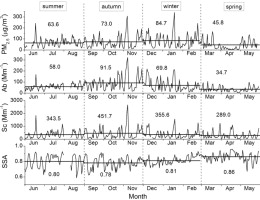
• Aerosol optical properties from 2009 to 2010 at an urban site in Beijing were investigated.
• Aerosol scattering and absorption were high in autumn and winter while low in summer and spring.
• Regional pollutants from south and southeast and local emissions dominated the aerosol pollution.
• Daily PM2.5 mass concentration should be controlled to lower than 64 μg/m3.
Year-round measurements of the mass concentration and optical properties of fine aerosols (PM2.5) from June 2009 to May 2010 at an urban site in Beijing were analyzed. The annual mean values of the PM2.5 mass concentration, absorption coefficient (Ab), scattering coefficient (Sc) and single scattering albedo (SSA) at 525 nm were 67 ± 66 μg/m3, 64 ± 62 Mm−1, 360 ± 405 Mm−1 and 0.82 ± 0.09, respectively. The bulk mass absorption efficiency and scattering efficiency of the PM2.5 at 525 nm were 0.78 m2/g and 5.55 m2/g, respectively. The Ab and Sc showed a similar diurnal variation with a maximum at night and a minimum in the afternoon, whereas SSA displayed an opposite diurnal pattern. Significant increases in the Ab and Sc were observed in pollution episodes caused by the accumulation of pollutants from both local and regional sources under unfavorable weather conditions. Aerosol loadings in dust events increased by several times in the spring, which had limited effects on the Ab and Sc due to the low absorption and scattering efficiency of dust particles. The frequency of haze days was the highest in autumn because of the high aerosol absorption and scattering under unfavorable weather conditions. The daily PM2.5 concentration should be controlled to a level lower than 64 μg/m3 to prevent the occurrence of haze days according to its exponentially decreased relationship with visibility.