- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
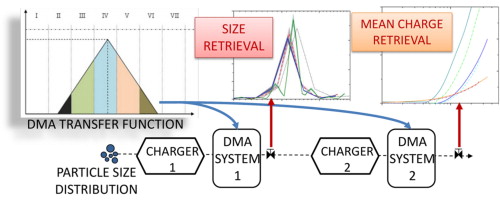
• Inversion of particle size distributions from electrical mobility data was analyzed.
• The transfer function in each size interval was geometrically estimated.
• Arbitrary voltage steps resulted in non-adjoining and overlapping transfer functions.
• Multiply charging was corrected to retrieve the singly charged particle distribution.
• Retrieval of the mean charge from a tandem DMA configuration was obtained.
The inversion of the particle size distribution from electrical mobility measurements is analyzed. Three different methods are adapted for a dot-matrix approach to the problem, especially for non-square or singular matrices, and applied to electrical mobility measurements from fixed or scanning voltages. Multiply charged particles, diffusion losses, arbitrary voltage steps and noise were considered, which results in non-adjoining and overlapping transfer functions. The individual contribution of the transfer functions in each size interval was geometrically estimated, which requires only its characteristic mobilities. The methodology is applied to mobility measurements from particles charged with unipolar and bipolar chargers. However, the method can be extrapolated to any charging method with a defined charge distribution, and retrieval of the singly charged particle distribution and mean charge from a tandem differential mobility analysis configuration was successfully demonstrated.