- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
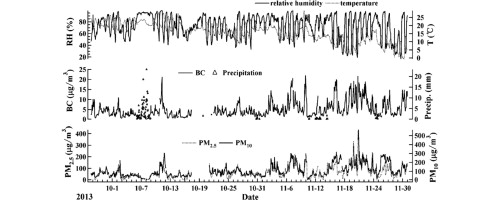
• Black carbon (BC) aerosol in Jiaxing, China was measured from Sep. 26 to Nov. 30, 2013.
• Temporal and diurnal variations of BC and influences of meteorology factors on BC were discussed.
• Absorption coefficient of BC was 44.4 Mm−1, constituting 11.1% of the total aerosol extinction.
We conducted measurements of black carbon (BC) aerosol in Jiaxing, China during autumn from September 26 to November 30, 2013. We investigated temporal and diurnal variations of BC, and its correlations with meteorological parameters and other major pollutants. Results showed that hourly mass concentrations of BC ranged from 0.2 to 22.0 μg/m3, with an average of 5.1 μg/m3. The diurnal variation of BC exhibited a bimodal distribution, with peaks at 07:00 and 18:00. The morning peak was larger than the evening peak. The mass percentages of BC in PM2.5 and PM10 were 7.1% and 4.8%, respectively. The absorption coefficient of BC was calculated to be 44.4 Mm−1, which accounted for 11.1% of the total aerosol extinction. BC was mainly emitted from local sources in southwestern Jiaxing where BC concentrations were generally greater than 11 μg/m3 during the measurement period. Correlation analysis indicated that the main sources of BC were motor vehicle exhaust, and domestic and industrial combustion.