- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Gas–solid distributor and upper fluidized bed imposed constraints on gas–solid flow in the riser.
• Effects of different operating conditions on constraint strength were investigated experimentally.
• Effect of constraint strength on particle velocity distribution in the coupled riser was studied.
• An empirical model describing the outlet constraint strength was established.
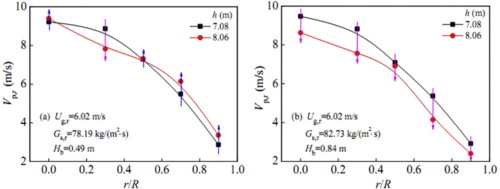
To study axial/radial profiles of particle velocity in the affected region of an integrated riser outlet, a cold model was developed for the integrated riser reactor combining the gas–solid distributor with the fluidized bed. Constraints, related to the gas–solid distributor and the upper fluidized bed, imposed on the particle flow in the riser outlet region, were investigated experimentally. The experimental results showed that with increasing superficial gas velocity, these constraints have strong influences on particle flow behavior, the particle circulation flux in the riser, and the height of the static bed material of the upper fluidized bed. When the constraints have greater prominence, the axial profile of the cross-sectionally averaged particle velocity in the outlet region initially increases and then decreases, the rate of decrease being proportional to the constraint strength. Along the radial direction of the outlet section, the region where the local particle velocity profile tends to decrease appears near the dimensionless radius r/R = 0.30 initially and then, with increasing constraint strength, gradually extends to the whole section from the inner wall. Based on the experimental data, an empirical model describing the constraint strength was established. The average relative error of the model is within 7.69%.