- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
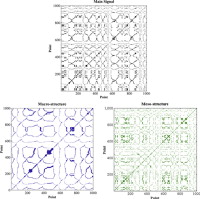
• DWT, RP and RQA were used to capture effect of immersed tubes on hydrodynamics of fluidized bed.
• Insertion of tubes affected flow structures more pronounced at low gas velocities.
• The RP of meso-structures was more similar to that of main signal.
• Results showed that bed became less periodic when tubes were inserted.
Multi-scale analysis and non-linear analysis were combined to investigate the hydrodynamics of fluidized beds with and without horizontal tubes. Pressure fluctuations were measured and analyzed employing discrete wavelet analysis, recurrence plot analysis, and recurrence quantification analysis. A systematic procedure was followed to determine wavelet parameters. At low gas velocities, the energy of macro-structures reduces with the addition of the first tube and then increases with the addition of a second tube. However, there is no notable difference at high gas velocities. Determinism is high for the bed without tubes, which can be attributed to the periodic behavior of bubbles. Determinism decreases with the addition of tubes because the breakage of bubbles results in less periodic behavior. The three methods of analysis used in this study captured the effects of immersed tubes on the hydrodynamics of fluidized beds. Recurrence quantitative analysis was found to be a powerful and easy-to-use method that can capture the nonlinear characteristics of fluidized beds much more quickly than conventional methods of nonlinear analysis. This method can thus be effectively used for the online monitoring of hydrodynamic changes in fluidized beds.