- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• The lattice Boltzmann method was employed to understand the mechanism of fibrous filters.
• Results of two regular arrangements of fibers and a random arrangement were compared.
• Several particle sizes and densities were considered.
• Effects of pertinent parameters on the pressure drop and capture efficiency were studied.
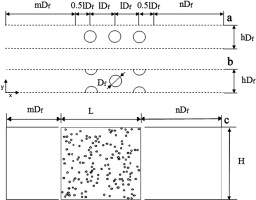
A fibrous filter is one of the most common systems used to separate suspended particles from air. Two important factors (i.e., the pressure drop and capture efficiency) are usually used to evaluate the performance of this type of filter. This study considers three two-dimensional arrangements of fibers (parallel, staggered, and random) to geometrically model fibrous media. The lattice Boltzmann method is employed to numerically simulate fluid flow through the filter. The Lagrangian form of the equation of motion of a particle is numerically solved to track the path of each particle in the flow field, where a one-way interaction between the fluid and particles is considered. The effects of pertinent parameters such as the fiber arrangement, solid volume fraction, particle-to-fiber diameter ratio, particle-to-fluid density ratio, Reynolds number, Stokes number, and size of the fibrous medium on the pressure drop and capture efficiency are studied. The obtained results are compared with existing empirical and theoretical findings and discussed.