- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
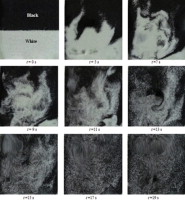
• Digital image processing method was applied to obtain the tracer concentration.
• Mixing rate was evaluated by analyzing the evolution of mixing index.
• A correlation was proposed to estimate the mixing rate in a small scale fluidized bed.
A new first degree solids mixing rate is proposed to evaluate the mixing of solids in small scale fluidized beds. Particle mixing experiments were carried out in a 2D fluidized bed with a cross-section of 0.02 m × 0.2 m and a height of 1 m. White and black particles with average diameters of 850 and 450 μm were used in our experiments. Image processing was used to measure the concentration of the tracers at different times. The effects of four representative operating parameters (superficial gas velocity, ratio of tracer particles to bed particles, tracer particle position, and particle size) on mixing are discussed with reference to the mixing index. We found that the Lacey index depends on the concentration of the tracers. The position of the tracers affects the initial mixing rate but not the final degree of mixing. However, the new mixing rate equation does not depend on the initial configuration of the particles because this situation is considered to be the initial condition. Using the data obtained in this work and that found in literature, an empirical correlation is proposed to evaluate the mixing rate constant as a function of dimensionless numbers (Archimedes, Reynolds, and Froude) in small scale fluidized beds. This correlation allows for an estimation of the mixing rate under different operating conditions and for the detection of the end point and/or the time of mixing.